Very Short Answer Questions - 1 Marks
Q1. Name the scientist who proved for the first time that objects move with constant speed when no force acts on them.
Ans. Galileo.
Q2. Why do bicycles begin to slow down when we stop pedaling?
Ans. This is because of the frictional forces acting opposite to the direction of motion
Q3. Which law of motion gives the measure of force?
Ans. Newton's second law of motion.
Q4. Write the C.G.S unit of force.
Ans. Dyne.
Q5. Can every force produce motion in every object?
Ans. No.
Q6. When a force is applied to a body, what are the two essential effect it can produce?
Ans. (a) It can bring about the change in the state of motion of a body or
(b) It can deform a body, i.e., it can change its shape.
Q7. Define 1 newton force.
Ans. 1 newton is the magnitude of force which produces an acceleration of I m/s2 in a body of mass 1 kg.
Q8. What do you mean by an impact force?
Ans. The force produced by the impact of a fast moving object on another is called impact force.
Q9. Define force of friction.
Ans. The force acting between any two surfaces in contact and tending to oppose motion is called force of friction.
Q10. Define electrostatic force.
Ans. The force exerted by an electrically charged body is called electrostatic force.
Q11. If the body is found to be accelerated, is the force acting on it balanced or unbalanced?
Ans. Unbalanced.
Q12. What do balanced forces usually do to a body?
Ans. Balanced forces usually produce a change in the shape of the body.
Q13. When a body moves on flat surface, will its speed change?
Ans. No.
Q14. What did Galileo conclude on the basis of his experiments on the motion of objects?
Ans. A body continues to move with the same velocity if no unbalanced force acts on it.
Q15. What do you mean by a resultant force?
Ans. When two or more forces act on a body simultaneously, then the single force which produces the same effect as produced by all the forces acting together is known as the resultant force.
Q16. Do action and reaction act on the same body?
Ans. No, action and reaction act on different bodies.
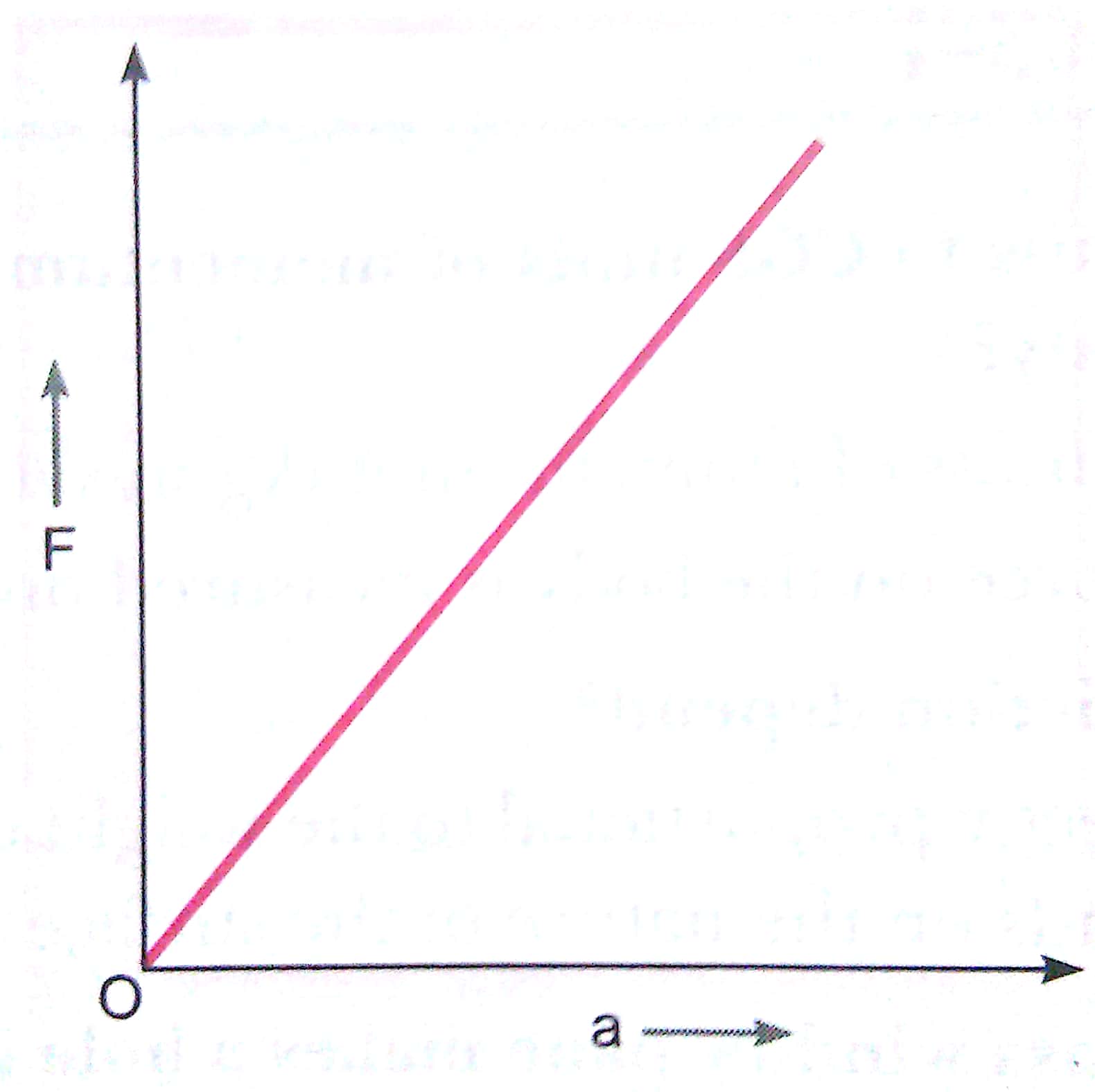
Q17. Plot a graph between force applied on a body and the acceleration produced in the given mass, assuming that the magnitude of force is constantly changing.
Ans.
Q18. Write the SI unit of impulse.
Ans. Ns.
Q19. What is the total momentum of a bullet and a gun before firing?
Ans. Zero.
Q20. Name the principle on which a rocket works.
Ans. Newton's third law of motion
Q21. Body A is heavier than body Q. Which has more inertia?
Ans. A has more inertia.
Q22. A body is moving with uniform acceleration. Is its momentum constant?
Ans. No.
Q23. Name the physical quantity that corresponds to the rate of change of momentum.
Ans. Force
Q24. Which principle is involved in the working of a jet plane?
Ans. Newton's third law of motion.
Q25. Why mass is sometimes called coefficient of linear inertia?
Ans. It is easier to pull a lighter body than a heavier body. Therefore, more the mass more will be the inertia. That is why mass is sometimes termed as coefficient of linear inertia.
Q26. When a force acting on a body has equal and opposite reaction, then why should the body move at all?
Ans. The action and reaction act on different bodies. Therefore, the body moves under the action of the acting force.
Q27. Does Newton's third law apply to a system where bodies do not actually touch each other?
Ans. Yes, whenever the bodies are in actual contact or even if there is an interaction between the bodies (e.g., attraction or repulsion between two magnets charges, etc.), Newton's third law is applicable.
Q28. Suppose a ball of mass m is thrown vertically upwards with an initial speed v, its speed decreases continuously till it becomes zero. Therefore, the ball begins to fall downward and attain the speed v again before striking the ground. It implies that the magnitude of initial and final momenta of the ball are same. Yet, it is not an example of conservation of momentum. Explain why.
Ans. Law of conservation of momentum is applicable to isolated system (no external force is applied), In this case, the change in velocity is due to the gravitational force of earth.

