Very Short Answer Questions - 1 Mark
Q.1. List two conditions which need to be satisfied for the work to be done on an object.
Ans. W = Fs
Work is done when
(a) a force acts on an object
(b) object is displaced.
Q.2. Explain the following terms with one example each:
(a) Positive work (b) Zero work
Ans. (a) When force acts in the direction of motion of body work done is positive. When a lawn roller is pulled forward, work done is positive.
(b) When force is perpendicular to the direction of motion, work done is zero. A porter carrying load does no work.
Q.3. From where do we get energy for the life processes?
Ans. The energy required for the various life processes comes from the food that we eat.
Q.4. A girl is running along a circular path with a uniform speed. How much work is done by the girl?
Ans. Zero.
Q.5. Moment of force and work done by a force have the same units. Then, what is the difference between them?
Ans. Moment of a force produces rotatory motion in a body whereas when a force does work on a body it produces translatory motion in it.
Q.6. A coolie is walking on a railway platform with a load of 27 kg on his head. What is the amount of work done by him?
Ans. Work done by the coolie is zero, as W = Fs cos 900 = 0.
Q.7. What is the amount of work done by a man in pressing a rigid wall with a force of 400 N?
Ans. Zero because there is no displacement.
Q.8. Which law was verified experimentally by James Prescott Joule?
Ans. Law of conservation of energy.
Q.9. State the law of conservation of energy.
Ans. The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, it can only be transformed from one form to another.
Q.10. Name the two common forms of mechanical energy.
Ans. Kinetic energy and potential energy.
Q.11. By what factor does the kinetic energy of a body increase when its speed is doubled?
Ans. By a factor of 4 (KE ∝ v2).
Q.12. What is negative work.
Ans. Work done against friction is a negative work.
Q.13. Out of a light and a heavy body having equal kinetic energy, which one will is move fast?
Ans. The lighter body because 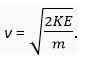
Q.14. What type of energy is stored in the spring of a watch?
Ans. Elastic potential energy.
Q.15. When an arrow is shot from its bow, it has kinetic energy. From where does it get this kinetic energy?
Ans. A stretched bow possesses potential energy on account of a change in its shape. When the arrow is released, the potential energy of the bow gets converted into the kinetic energy of the arrow.
Q.16. Can kinetic energy of a body be negative?
Ans. No, because both m and v2 are always positive.
Q.17. An electric cell converts which form of energy into which other form?
Ans. Chemical energy gets converted into electrical energy.
Q.18. Which instrument transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy?
Ans. Electric motor.
Q.19. When an electric bulb is switched on, what energy transformation takes place?
Ans. Electric energy changes into light energy and heat energy.
Q.20. What kind of energy transformation takes place at thermal power station?
Ans. Heat energy is converted into electrical energy.
Q.21. A car is accelerated on a levelled road and attains a velocity four times its initial velocity. In this process, how does the potential energy of the car change?
Ans. Potential energy (= mgh) does not change as it does not depend on velocity.
Q.22. What is the angle between the force and displacement in the case of negative work?
Ans. 1800.
Q.23. A student picks up four books from the floor, walks across the room through some distance with the books at the same height and then keeps these books at the new place. In which of these sequence of actions work is said to be performed?
Ans. When the student is picking up books from the floor in the beginning.

