Very Short Answer Questions - 1 Mark
Que 1. What is light?
Ans. Light is a form of energy which gives us the sensation of sight or vision.
Que 2. What is a ray of light?
Ans. The path along which light travels is called a ray of light.
Que 3. What is a beam of light?
Ans. A group of light rays originating from a source and travelling in some definite direction is known as a beam of light.
Que 4. Name a communication device which uses light for its working.
Ans. Optical fibres, which transmit many telephonic messages at the same time.
Que 5. What is the angle of reflection when a ray of light falls normally on a plane mirror?
Ans. The angle of reflection is 0°.
Que 6. What kind of image can be obtained on the screen?
Ans. Real image
Que 7. What type of image is formed:
(i) in a plane mirror, and (ii) on a cinema screen?
Ans. Virtual image, and (i) real image.
Que 8. Name the type of mirror which always forms a virtual and diminished image.
Ans. Convex mirror.
Que 9. Which mirror-convex or concave has larger field of view?
Ans. Convex mirror.
Que 10. If an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, where is the image formed?
Ans. At infinity.
Que 11. What should be the position of the object when a concave mirror is to be used:
(i) as a shaving mirror?, and (ii) as a doctor's mirror?
Ans. (i) Between pole P, and focus F, and
(ii) At focus F.
Que 12. What sign (+ve or-ve) is given to the focal length of:
(a) a concave mirror?, and (b) a convex mirror?
Ans. (a) Focal length of a concave mirror is - ve, and
(b) Focal length of a convex mirror is + ve.
Que 13. Give the cartesian sign convention for:
(a) height of a real image, and (b) height of a virtual image.
Ans. (a) - ve, and (b) + ve.
Que 14. What is the significance of +ve sign of magnification?
Ans. + ve sign of magnification shows that the image is virtual and erect.
Que 15. Can a plane mirror be called spherical mirror?
Ans. Yes, a plane mirror can be called a spherical mirror of infinite radius of curvature.
Que 16. A man standing in front of a spherical mirror, finds his image having a very small head, a fat body and legs of normal size. What type of mirrors are used in these three parts?
Ans. A very small head: Convex mirror,
A fat body: Concave mirror, and
Legs of normal size: Plane mirror
Que 17. Differentiate between virtual image formed by a concave mirror and of a convex mirror.
Ans. The virtual image formed by a concave mirror is always magnified whereas the virtual image formed by a convex mirror is diminished.
Que 18. What is the magnification produced by a plane mirror?
Ans. The magnification of a plane mirror is 1.
Que 19. The angle between an incident ray and the mirror is 40°.
(i) What is the angle of incidence?
(ii) What is the angle of reflection?
(iii) What is the total angle through which the ray of light turns?
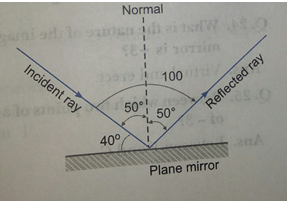
Ans. (i) 50°
(ii) 50°
(iii) 100°
Que 20. Why does a convex mirror is said to have a virtual principal focus?
Ans. In a convex mirror, the reflected rays do not actually pass through the focus (F). So, a convex mirror has a virtual principal focus, which is situated behind the mirror.
Que 21. What is the value of θ in the following ray diagram?
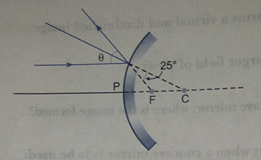
Ans. Θ = 25 + 25 = 50°
Que 22. Explain why a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror gets reflected along the same path after reflection.
Ans. This is because the angle of incidence is 0°. That is the ray passing through the centre of curvature is incident normally to the mirror. The angle of reflection should also be 0°.
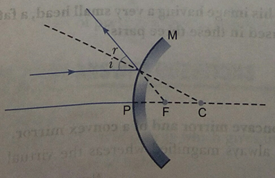
Que 23. Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Ans.
Que 24. What is the nature of the image formed by a concave mirror if the magnification product by the mirror is +3?
Ans. Virtual and erect.
Que 25. Between which two points of a concave mirror should an object be placed to obtain a magnification of-3?
Ans. Between F and C.
Que 26. The outer surface of a hollow sphere of aluminium of radius 50 cm is to be used as a mirror. What will be the focal length of this mirror? Which type of spherical mirror will it provide?
Ans. Focal length, 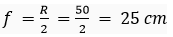
It will provide convex mirror.
Que 27. Which property of concave mirror is utilised for using them as shaving mirrors?
Ans. When an object is placed between the pole and focus of concave mirror a magnified, erect and virtual image is obtained.
Que 28. What is an optically rarer medium?
Ans. A medium in which light travels comparatively faster than the other medium is called an opticallyrarer medium.
Que 29. What is an optically denser medium?
Ans. A medium in which light travels comparatively slower than the other medium is called an opticallydenser medium.
Que 30. Define the term refraction of light.
Ans. The bending of a ray of light falling obliquely on a surface when it passes from one medium to another is called refraction.
Que 31. Define the term angle of incidence.
Ans. The angle between an incident ray and the normal at the point of incidence is called angle of refraction.
Que 32. Define the term angle of refraction.
Ans. The angle between the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence is called angle of refraction.
Que 33. Define the term refractive index of a medium in terms of speed of light.
Ans. Refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the medium. i.e.,
Refractive index (of a medium) = 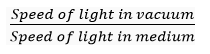
Que 34. What is absolute refractive index?
Ans. Refractive index of a medium with respect to vacuum is called absolute refractive index.
Que 35. What is relative refractive index?
Ans. Refractive index of a medium with respect to another medium is called relative refractive index.
Que 36. What is the unit of refractive index?
Ans. Refractive index has no units as it is a ratio of two similar physical quantities.
Que 37. Refractive index of two material mediums X and Y are 1.3 and 1.5 respectively. In which of the two, the light would travel faster?
Ans. In medium 'X' because of lower value of refractive index.
Que 38. What is the cause of refraction of light?
Ans. Refraction of light takes place when it travels from one medium to another because the speed of light is different in the two media.
Que 39. What is the relationship between the refractive index of two media?
Ans. The refractive index for the light going from medium '1'to medium ‘2’ is equal to the reciprocal of the refractive index for light going from medium ‘2’ to medium ‘1’.
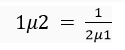
Que 40. In which direction a ray of light bends when it goes from water to glass?
Ans. We know that glass is denser medium than water. Therefore, a ray of light will bend towards the normal when it goes from water to glass.
Que 41. If refractive indices of water and alcohol are 1.33 and 1.36 respectively, which of the two is optically denser medium?
Ans. The refractive index of alcohol is more than water, therefore, alcohol is optically denser medium.
Que 42. If a light ray IM is incident on the surface AB as shown, identify the correct emergent ray.
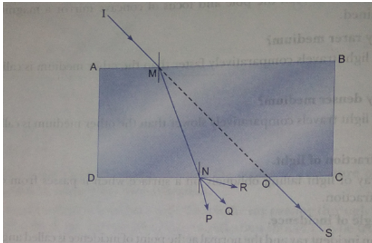
Ans. Here, NQ is parallel to OS. Therefore, NQ is the correct emergent ray.
Que 43. Why does a ray of light bend when it travels from one medium into another?
Ans. When a ray of light travels from one medium to another, its speed changes and this in speed of light causes the bending of light (refraction of light).
Que 44. What is a lens?
Ans. A lens is a piece of transparent medium bounded by two spherical surfaces.
Que 45. Name a point inside a lens such that a ray of light passing through it goes undeviated.
Ans. Optical centre.
Que 46. Name the phenomena on which the working of a lens is based.
Ans. The working of a lens is based on the phenomenon of refraction of light.
Que 47. State two examples of phenomenon of refraction of light in everyday life situations.
Ans. (i) A stick partly immersed in water appears to be bent at the water surface.
(ii) A pool of water appears less deep than it actually is.
Que 48. What is meant by power of a lens?
Ans. Ans. power of a lens is the degree of convergence or divergence of light rays achieved by a lens, 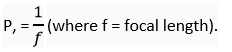
Que 49. Give the SI unit of power of lens. State whether the power of a converging lens is positive or negative.
Ans. The SI unit of power of a lens is dioptre.
The power of a converging lens is positive as f is +ve.
Que 50. A spherical mirror and a lens have same focal length of-20 cm. What type of mirror and lens are these?
Ans. A concave mirror and concave lens have negative focal length. Hence, both mirror and lens are concave.
Que 51. A small electric lamp is placed at the focus of a convex lens. What is the nature of beam of light produced by the lens?
Ans. The beam of light coming out of lens is parallel beam of light as shown.
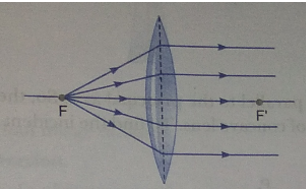
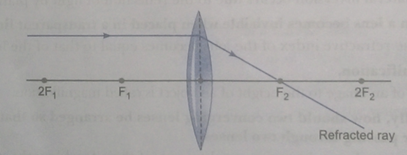
Que 52. An object is placed 80 cm from a converging lens of focal length 25 cm. What is the nature of the image?
Ans. The image is real, inverted and diminished as the object is placed beyond 2F.
Que 53. What is the power of a combination of lenses?
Ans. If a number of lenses are placed in close contact, then the power of the combination of lenses is equal to algebraic sum of the powers of the individual lenses.
P = PI + P2
Que 54. State one advantage of using combination of lenses in optical instruments instead of a lens.
Ans. The use of a combination of lenses increases the sharpness of the image.
Que 55. What is monochromatic light?
Ans. The light of a single wavelength is called monochromatic light, e.g., Sodium lamp is a source of monochromatic light.
Que 56. Name the component of white light that has the greatest wavelength.
Ans. Red.
Que 57. How does phenomenon of lateral inversion occurs?
Ans. The phenomenon of lateral inversion occurs due to the reflection of light by plane mirror.
Que 58. Under what condition a lens becomes invisible when placed in a transparent liquid?
Ans. This happens when the refractive index of the lens becomes equal to that of the liquid.
Que 59. Define the term magnification.
Ans. The ratio of the height of an image to the height of an object is called magnification.
Que 60. Show diagrammatically, how should two converging lenses be arranged so that a parallel beam becomes parallel after passing through two lenses.
Ans. If the distance between two lenses becomes equal to sum of their focal lengths, then the parallel beam of light will emerge parallel after passing through the second lens.
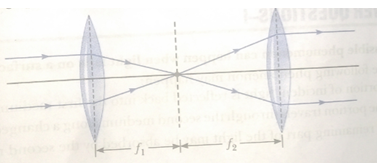
Que 61. The diagram below shows the refracted ray QR through a concave lens. Complete the diagram by drawing the corresponding incident ray.
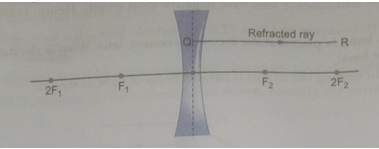
Ans. In figure the refracted ray parallel to the principal axis. So, the Incident ray must be appearing to meet at the principal focus of concave lens. To find the incident ray, F2 is joined to Q and produced as shown in the figure.
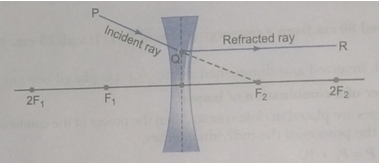
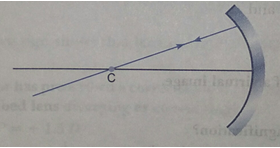
Que 62. Redraw the given diagram and show the path of the refracted ray.
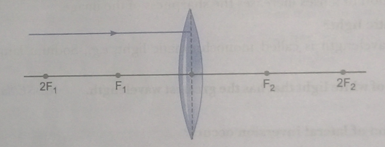
Ans.