Very Short Answer Questions - 1 Mark
Que 1. Draw the electron dot structure of the gas molecule which is liberated when zinc metal is treated with aqueous NaOH solution.
Ans. Hydrogen gas, 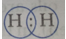
Que 2. Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of ethane.
Ans. There are seven covalent bonds: 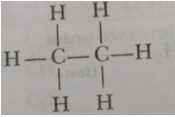
Que 3. Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of propane, C3 H8.
Ans. There are ten covalent bonds: 
Que 4. Write the number of covalent bonds in the molecule of butane, C4H10.
Ans. There are thirteen covalent bonds: 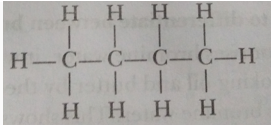
Que 5. Which element exhibits the property of catenation to maximum extent and why?
Ans. Carbon exhibits the property of catenation due to strong C–C bond.
Que 6. What is the molecular formula of the alcohol which can be derived from propane?
Ans. Propane: CH3 – CH2 – CH3 or C3 H8
Alcohol obtained from propane is C3H7OH.
Que 7. Give the names of the functional groups:
(i) –OH (ii) 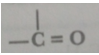
Ans. (i) Alcoholic group (ii) Ketonic group.
Que 8. Which functional group always occur at the terminal position of a carbon chain?
Ans. Aldehydic group R–CHO and carboxyI group R–COOH (R = alkyl group).
Que 9. Name the function group which always occurs in the middle of a carbon chain.
Ans. Ketonic group always occurs in the middlr of a carbon chain.
Que 10. In an organic compound, which parts largely determine its physical and chemical properties?
Ans. The alkyl part (carbon chain) of an organic compound determines its physical properties whereas the functional group determines its chemical properties.
Que 11. An organic compound 'X' of molecular formula C2H4O2 gives brisk effervescence with sodium bicarbonate. Give the name and formula of X.
Ans."X' is ethanoic acid (an organic acid). 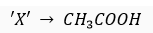
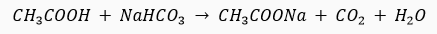
Organic acid decomposes sodium bicarbonate and gives brisk effervescence of carbon dioxide gas.
Que 12. Why is pure ethanoic acid called glacial ethanoic acid (or glacial acetic acid)?
Ans. The melting point of pure ethanoic acid is 290 K and hence it often freezes in cold climate to form a colourless, ice-like liquid. This has given it the name glacial acetic acid.
Que 13. What is vinegar?
Ans. A 5-8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar and is used widely as a preservative in pickles.
Que 14. How does carbon attain a stable electronic configuration?
Ans. Carbon attains stable electronic configuration by sharing its four electrons with other atoms.
Que 15. What is isomerism?
Ans. It is a phenomenon in which compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formula.
Que 16. Which of the following formulae represents a saturated hydrocarbon?
CnH2n+ , CnH2n + 1, CnH2n , CnH2n- 2
Ans. Cn H2n + 2 represent a saturated hydrocarbon.
Que 17. Which of the following are alkenes?
CH4, C2H6, C2H4, C3H6 and C3H8.
Ans. C2H4 and C3H6 are alkenes.
Que 18. What happens when methane is burnt in air?
Ans. Methane burns in air to give carbon dioxide and water.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + Heat energy.
Que 19. A test tube contains a brown coloured liquid. The colour of the liquid in test tube remains uncharged when methane is passed through it, but disappears when ethene is passed . Which element is present in the liquid?
Ans. The element present in the liquid is bromine.
Que 20. What is the next homologue of C3H7OH called?
Ans. The next homologue of C3 H7 OH is called butanol (C4 H9 OH).
Que 21. Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n.
Ans. The 2nd member is propene, C3H6.
Que 22. Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n+ 2.
Ans. The second member is ethane, C2H6.
Que 23. Write the name and formula of the 2 nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n-2.
Ans. The 2nd member is propyne, C3H4.
Que 24. Which two of the following organic compounds belong to the same homologous series?
C2H6, C2H6O, C2H6O2, CH4O
Ans. CH4O and C2H6O belong to the same homologous series.
Que 25. Write the name and molecular formula of the first member of the homologous series of alkynes.
Ans. The first member is ethyne, C2H2.
Que 26. Write the name and molecular formula of the fourth member of alkane series.
Ans. The fourth member of the alkane series is butane C4H10.
Que 27. Write the next homologue of each of the following:
(i) C2H4 (ii) C4H6
Ans. (i) C3H6 (ii) C5H8
Que 28. Name the following compounds:
(a) CH3 - CH2- OH
(b) 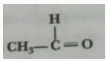
Ans. (a) Ethanol (b) Ethanal
Que 29. Select saturated hydrocarbons from the following:
C3H6; C5H10; C4H10; C6H14; C2H4
Ans. C4H10 and C6H14 are saturated hydrocarbons.
Que 30. Write the name and structure of an alcohol with three carbon atoms in its molecule.
Ans. The compound is propanol.

Que 31. Write the name and structure of an aldehyde with four carbon atoms in its molecule.
Ans. Butanal; 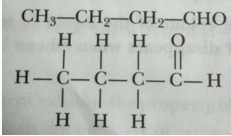
Que 32. Name the process by which unsaturated fats are changed to saturated fats.
Ans. Hydrogenation

