Short Answer Questions – II - 3 Marks
Q1. Write three differences between transverse waves and longitudinal waves.
Ans.
| Transverse Waves | Longitudinal Waves |
| 1. The particles of the medium oscillates up and down about their mean position. | 1. The particles of the medium move in the parallel to the direction of propagation of the disturbance. |
| 2. They propagate as crests and troughs. | 2. They propagate as compressions and rarefactions. |
|
3. The propagation of waves is possible in solid or surface of liquid but not in gases. Example: Light wave |
3. The propagation of these waves is possible in solids, liquids and gases. Example: Sound wave |
Q. 2. Prove that 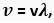 where the symbols have their usual meanings.
where the symbols have their usual meanings.
Ans. Let the time period of a wave be T seconds.
In T seconds, number of waves generated = 1.
So, in I second number of waves generated 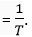
But number of waves generated in 1 second is frequency.
∴ 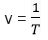
Now, 
⇒ 
⇒ 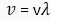
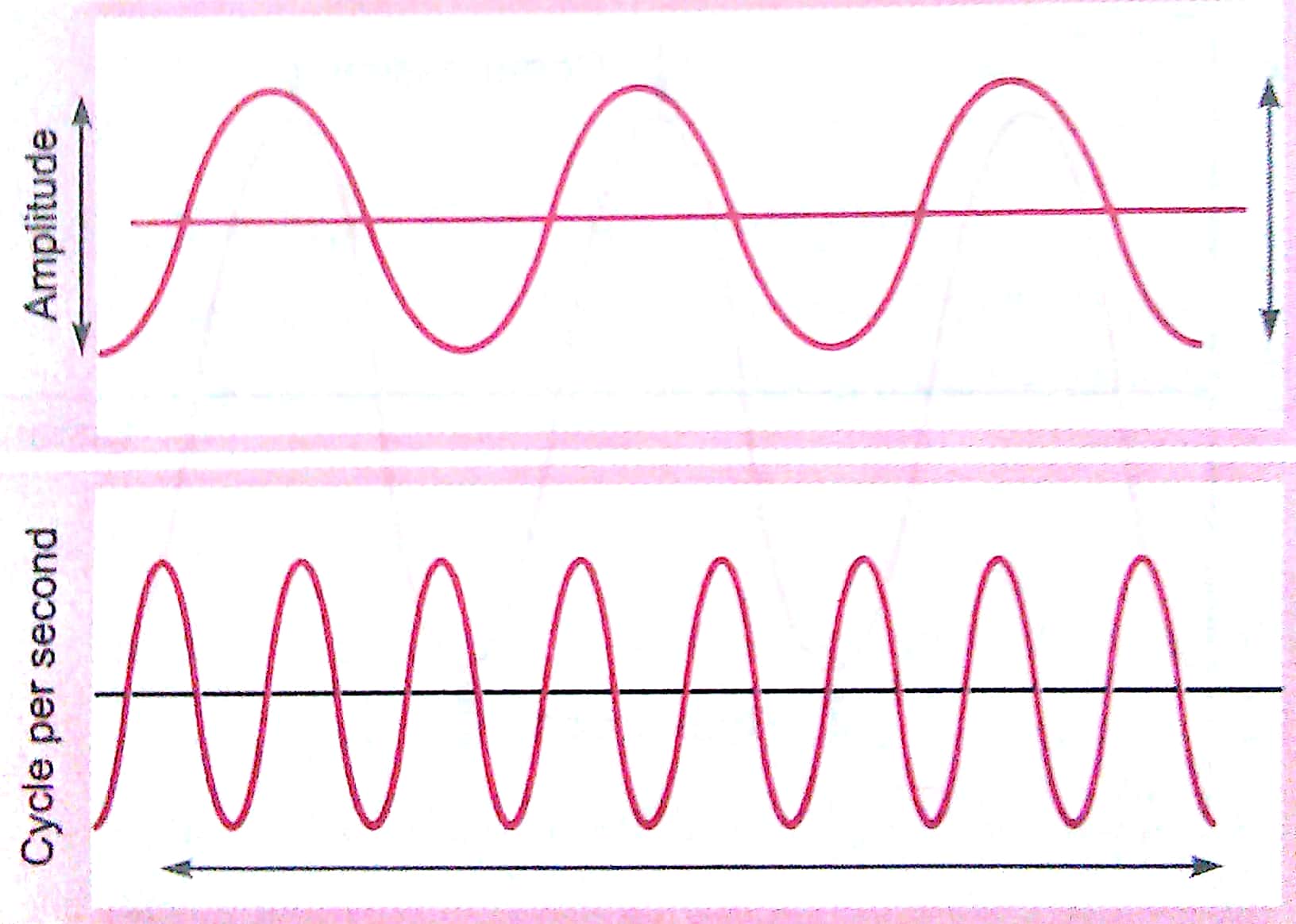
Q3. Which wave characteristics determine the (a) loudness (b) pitch of sound? Draw two different waveforms and mark these characteristics on it.
Ans. (a) Amplitude
(b) Frequency
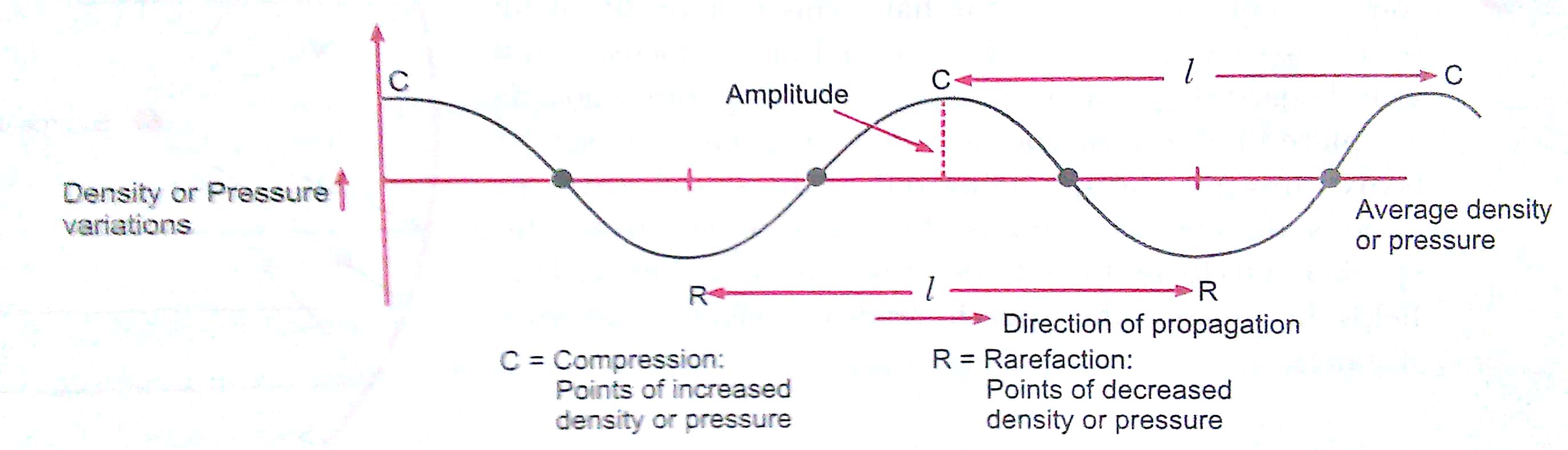
Q4. Plot the following:
(i) A longitudinal wave in air on a density-distance graph.
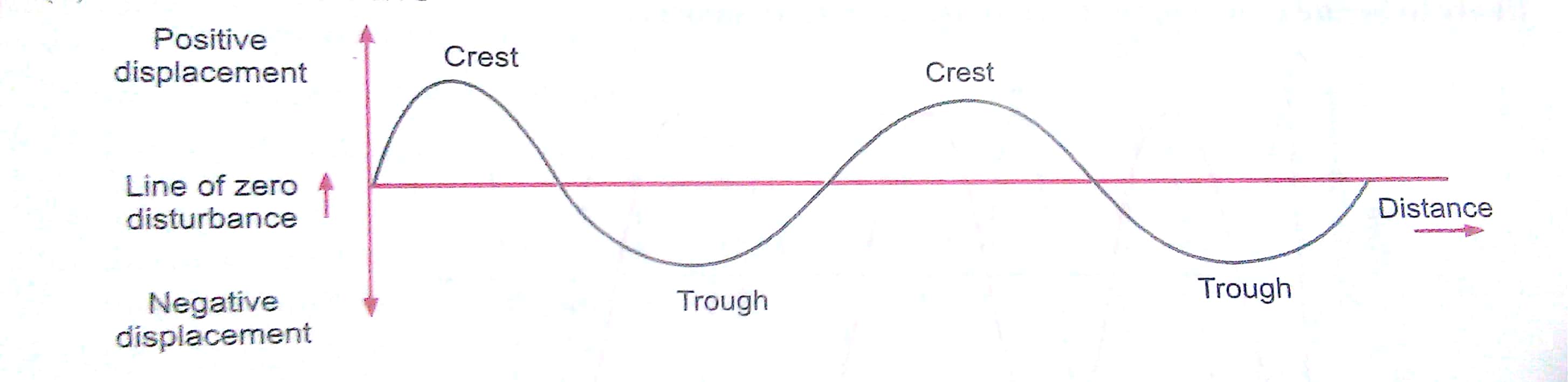
(ii) A transverse wave on a displacement-distance graph.
Ans. (i) A longitudinal wave in air
(ii) A transverse wave
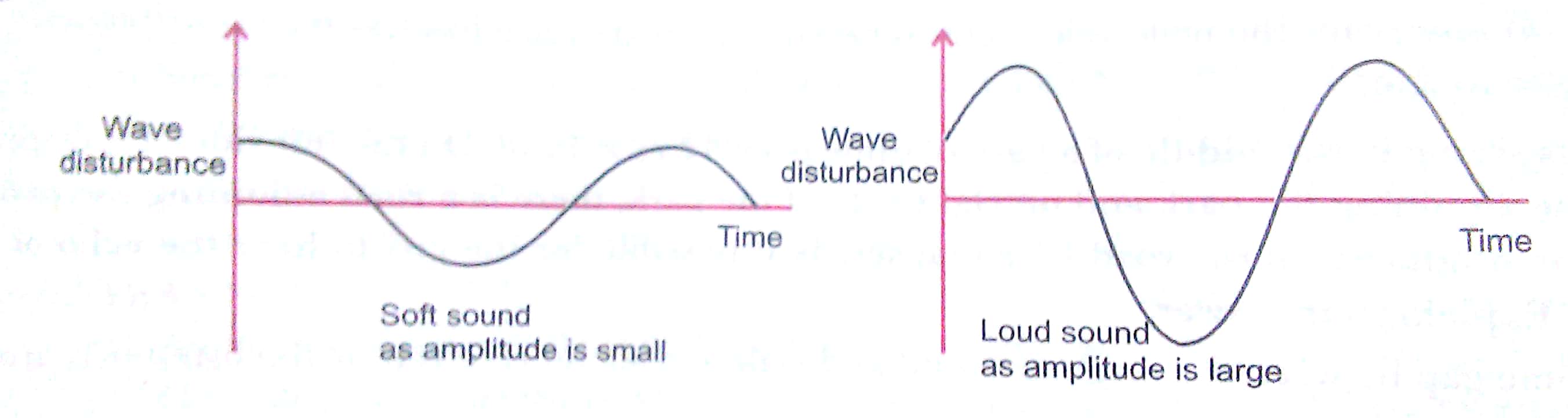
Q5. Draw diagrams to represent soft sound and loud sound.
Ans.
Q6. Write full form of acronym SONAR. Explain how the method of echo- ranging is used to determine the depth of sea.
Ans. Sound Navigation And Ranging: A transmitter producing ultrasonic waves is fitted at the bottom of a ship or a boat. The ultrasound waves emitted by the transmitter go to the bottom of the sea and get reflected from the bottom. These are received back by a detector also fitted at the bottom. Knowing the time elapsing between sending and receiving back of the ultrasonic waves and the speed of these waves in water, the depth of sea can be calculated.
Q7. What is a sound board? Explain the working of a soundboard with the help of a labelled diagram.
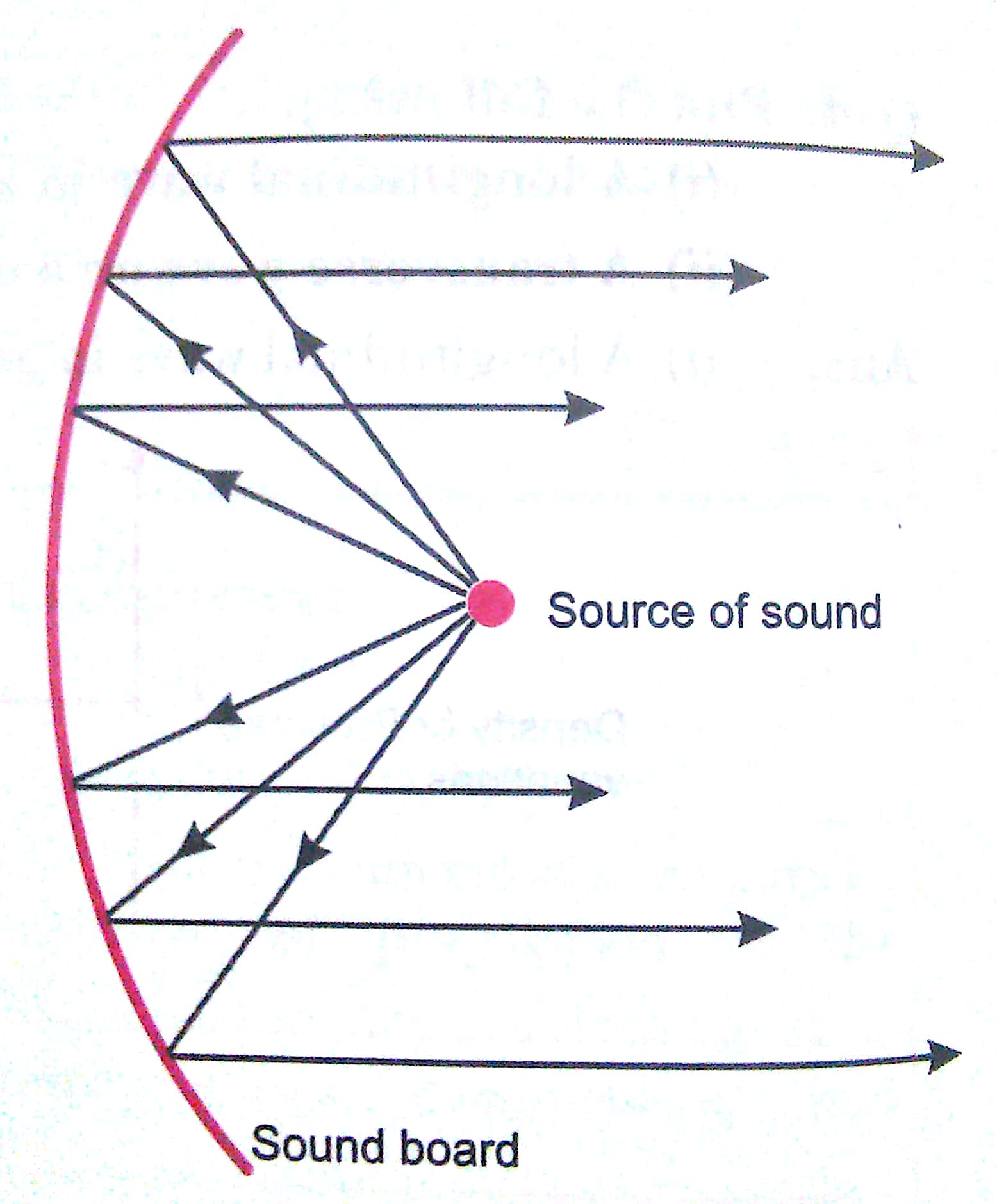
Ans. The reflection of sound may take place at curved surfaces also. This fact is made use of in the large halls to spread sound evenly throughout the hall. This is done by using sound boards. The speaker is located at the focus of the sound board (Fig.) and the concave reflecting sound boards are placed behind the speakers in a large hall. The sound board prevents the spreading out of the sound waves in various directions. It sends the sound waves from the speaker at its focus, by reflection towards the audience. This helps in making the speech readily audible even at a distance.
Q. 8. In the graphs given below representing the human voice, which of the two graphs (a) or (b) is likely to be the male voice? Give reason for your answer.
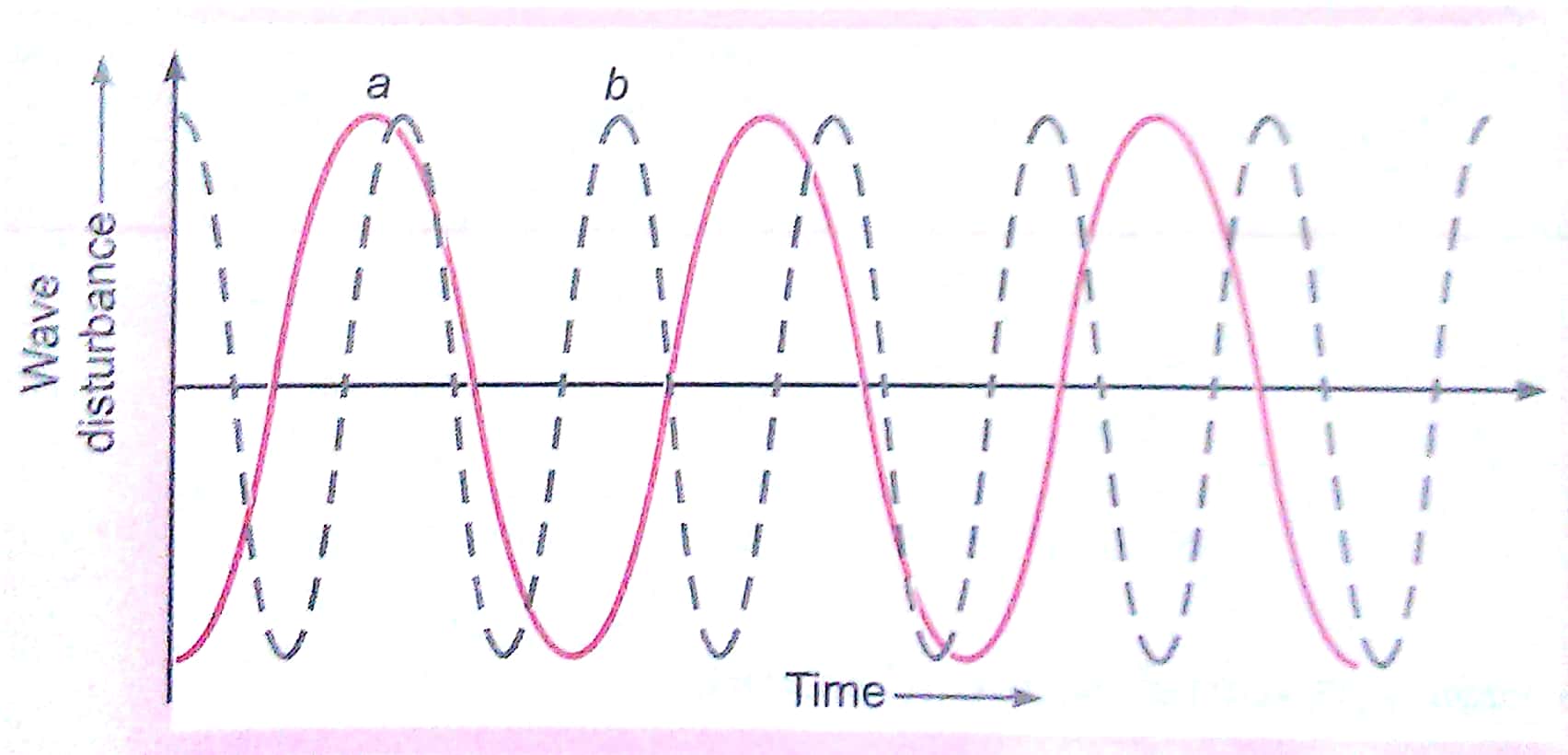
Ans. Graph (a) represents the male voice. This is because the male voice has less pitch (or frequency) as compared to female.
Q9. A girl is sitting in the middle of a park of dimension 12 m x 12 m. On the left side of it there is a building adjoining the park and on right side of the park, there is a road adjoining the park. A sound is produced on the road by a cracker. Is it possible for the girl to hear the echo of this sound? Explain your answer.
Ans. If the time gap between the original sound and reflected sound received by the listener is around 0.1 s, only then the echo can be heard.
The minimum distance travelled by the reflected sound wave for the distinctly listening the echo
= Velocity of sound × Time interval
= 344 x 0.1 = 34.5 m
But in this case the distance travelled by the sound reflected from the building and then reaching to the girl will be (6 + 6) = 12 m, which is much smaller than the required distance. Therefore, no echo can be heard.
Q. 10. A disused railway line has a length of 300 m. A man puts his ear against one end of the rail and another man hits the other end with a metal hammer, as shown in figure.
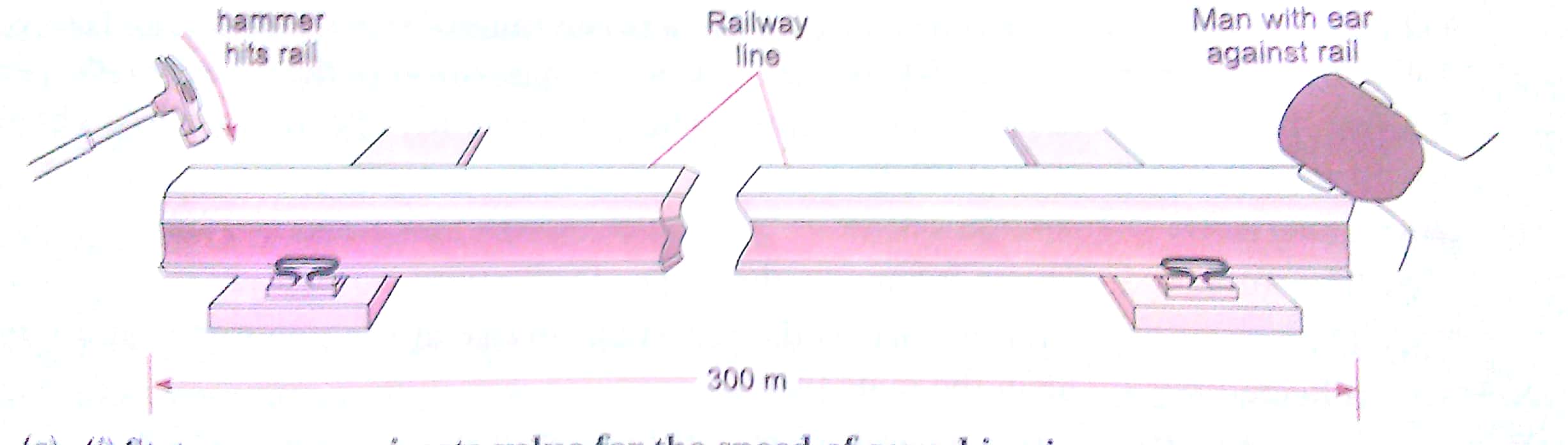
(a) (i) State an approximate value for the speed of sound in air.
(ii) Sound travels at 5000 m/s in steel. Calculate the time it takes for the sound to travel along the rail.
(b) The man with his ear to the railway line actually hears two sounds from the hammer, separated by a short interval. Explain why he hears two sounds.
Ans.
(a) (i) The approximate value for the speed of sound in air is 344 m/s
(ii) Distance = 300 m, Speed = 5000 m/s
∴ 
(b) As we know, the speed of sound is different in different materials. Sound travels about 15 times faster in steel than in air. The man hears two sounds one through air and other through railway line made of steel.
Q11. Give reasons for the following:
(a) The reverberation time of a hall used for speeches should be very short.
(b) A vibrating body produces sound. However no sound is heard when a simple pendulum oscillates in air.
(c) Sounds of same loudness and pitch but produced by different musical instruments like a violin and flute are distinguishable.
Ans. (a) If the reverberation time of a hall is long, then the multiple echoes will enterfere with original sound. For this reason nothing will be heard distinctly. So, the reverberation time of the hall should be very short.
(b) A sound is heard only if the body vibrates with a frequency more than 20 Hz and less than 20,000 Hz. The pendulum oscillates with a frequency less than 20 Hz. Hence, no sound is heard.
(c) This is due to the quality or timbre of sound waves.

