Short Answer Questions – II - 3 Marks
Q. 1. Suppose that the radius of the earth becomes twice of its original radius without any change in is mass. Then what will happen to your weight?
Ans. We know that 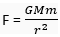 as weight of a body is the force with which a body is attracted towards the earth,
as weight of a body is the force with which a body is attracted towards the earth,
∴ 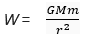
If the radius of the earth becomes twice of its original radius, then
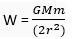
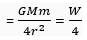
i.e., weight will be reduced to one-fourth of the original.
Q. 2. Prove that if the earth attracts two bodies placed at same distance from the centre of the earth with the same force, then their masses are equal.
Ans. Let P and Q be the two bodies,
the mass of body P = m1
And the mass of body Q = m2
As per the universal law of gravitation, the force of attraction between the earth and the body P is given by,
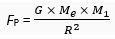 … (1)
… (1)
Where, R is the distance of the body from the centre of the earth.
Similarly, the force of attraction between the earth and the body Q is given by
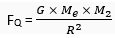 … (2)
… (2)
Since, the two forces, i.e., FP and FQ are equal, thus from (1) and (2),
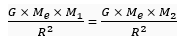
Q3. Give three differences between acceleration due to gravity (g) and universal gravitational constant (G).
Ans. Differences between g and G
|
Acceleration due to gravity (g) |
Universal gravitational constant (G) |
|
1. Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration acquired by a body due to the earth’s gravitational pull on it. 2. g is a vector quantity. 3. It is different at different places on the surface of the earth. Its value also varies from one celestial body to another. |
1. Gravitational constant is numerically equal to the force of attraction between two masses of 1 kg that are separated by a distance of 1 m. 2. G is a scalar quantity. 3. The 'G' is a universal constant, i.e., its value is the same (i.e. 6.7 x 10-11 Nm2 kg-2) everywhere in the universe. |
Q. 4. On the earth, a stone is thrown from a height in a direction parallel to the earth's surface while another stone is simultaneously dropped from the same height. Which stone would reach the ground first and why?
Ans.
For both the stones
Initial velocity, u = 0
Acceleration in downward direction = g
Now, 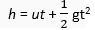
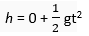
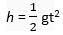
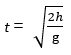
Both stones will take the same time to reach the ground because the two stones fall from the same height.
Q. 5. Calculate the average density of the earth in terms of g, G and R.
Ans. we know that 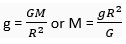
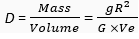
(Where V e is the volume of the earth)
or 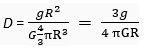
Q. 6. Prove that if a body is thrown vertically upward, the time of ascent is equal to the time of descent.
Ans. Upward motion
v = u – gt1
0 = u – gt1
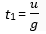 … (1)
… (1)
Downward motion
v = u + gt2
v = 0 + gt2
As the body falls back to the earth with the same velocity it was thrown vertically upwards.
∴ v = u
v = 0 + gt2
t2 = u/g … (2)
From (1) and (2), we get t1 = t2
Q. 7. Two objects of masses m1 and m2 having the same size are dropped simultaneously from heights h1 and h2, respectively. Find out the ratio of time they would take in reaching the ground. Will this ratio remain the same if (i) one of the objects is hollow and the other one is solid; and (ii) both of them are hollow, size remaining the same in each case? Give reasons.
Ans. As 
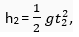
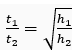
Ratio will not change in either case because acceleration remains the same. In case of free fall acceleration does not depend upon mass and size.

