Short Answer Questions – II - 3 Marks
Q1. What is a species? Give its main features.
Ans. Species is defined as a dynamic group of organisms, which resemble each other in all essential aspects, i.e., structure and function, and interbreed to produce fertile young ones of their own kind. The members of a species are reproductively isolated from other groups. They have descended from a common ancestor and have similar genetic material.
Q.2. State reasons for each of the following:
(i) Echidna and platypus lay eggs but are considered as mammals.
(ii) Forelimbs of birds are modified.
(iii) Crocodiles have four-chambered heart but are still reptiles.
Ans.
(i) They have mammary glands for the production of milk to nourish their young ones.
(ii) To reduce body weight for flight, forelimbs of birds are modified.
(iii) Crocodiles are cold blooded, lay eggs and have scale on their body. These characteristics make them reptile.
Q3. Differentiate between species and taxon.
Ans. Species and taxon differ in the following ways:
(i) Species represents the basic taxonomic category while the taxon represents any level of taxonomic category.
(ii) Species is always monophyletic while a taxon may be monophyletic or polyphyletic.
(iii) Species, being a rank, is an abstract term while a taxon represents a group of various living being.
Q4. Give the general characters of kingdom Animalia.
Ans.
(i) In kingdom Animalia, all the members are multicellular eukaryotes with tissue differentiation.
(ii) They are heterotrophic with ingestive mode of intake of food.
(iii) They possess a well developed nervous system.
(iv) Muscular system is also well developed for locomotion.
(v) They exhibit sexual reproduction.
Sponge, molluscs, fishes, birds, reptiles and mammals all belong to kingdom Animalia.
Q5. Enlist the main features of organisms placed under Protista.
Ans.
(i) Most of the members are unicellular and primarily aquatic.
(ii) They have nucleus and typical eukaryotic cell organelles.
(iii) Most of the organisms bear flagella or cilia for movements.
(iv) Mode of nutrition is absorptive, ingestive or photo-autotrophic.
(v) Reproduction may be asexual or sexual.
Q6. Give the main features of kingdom Fungi.
Ans.
(i)They are non-green because of the absence of chlorophyll.
(ii) They are heterotrophic and obtain food from dead and decaying organic matter by absorption
(iii) The body organisation is mycelial or secondarily unicellular.
(iv) Cell wall is chitinous and cellulosic.
(v) Asexual reproduction is by spore formation. Some also exhibit sexual reproduction.
Q7. Write the main characteristics of kingdom Plantae.
Ans.
(i)They are all complex multicellular plants which prepare their own food by photosynthesis.
(ii) They possess cell wall made of cellulose.
(iii) Plants are immobile and do not show locomotion.
(iv) They have unlimited growth and grow throughout their lives.
Q8. Write similarities between plants and animals.
Ans.
(i) Plants and animals are both made up of cells.
(ii) Both contain protoplasm and the genetic material, DNA.
(iii) Both plants and animals show growth.
(iv) Both show response to external stimuli.
(v) Both plants and animals reproduce and pass on their characters to the offspring by the same mechanism.
Q9. Give the main features of algae.
Ans.
(i) They are autotrophic as they possess chlorophyll.
(ii) They are mainly aquatic but some also grow in moist places.
(iii) The body is not divided into root, stem and leaves.
Q10. Give the important features of division Bryophyta.
Ans.
(i) Bryophytes are called the amphibians of the plant kingdom.
(ii) The plant body is commonly differentiated to form stem and leaf-like structures. But there is no specific tissue for conduction of water and other substances.
(iii) Vegetative reproduction is very common.
(iv) Sexual reproduction is of oogamous type, i.e., the male gamete is small and motile and female gamete is non-motile and large, e.g., moss, Funaria and Marchantia.
Q 11. Give the main features of Pteridophyta.
Ans. Following are the main features of Pteridophyta:
(i) The plant body is divided into root, stem and leaves.
(ii) The fertilised eggs form embryo.
(iii) They are also called vascular cryptogams as they have a developed vascular system.
(iv) They have multicellular reproductive system.
Q12. Give the important features of class Mammalia.
Ans. The important features of class Mammalia are:
(i) They are warm-blooded animals
(ii)Their heart is four-chambered.
(iii) They have mammary glands which produce milk with which they nourish their young ones.
(iv) They give birth to young ones, with the exception of platypus and echidna. Kangaroos give birth to very poorly developed young ones.
Q13. Blue green algae have been included under the group Monera and not under Plantae. why?
Ans. Monera is a kingdom of prokaryotes while organisms of kingdom Plantae are eukaryotes with definite nucleus, membrane-bound organelles and multicellular body design. Blue-green algae are prokaryotes having nucleoid with naked DNA. The cell organelles are also not enclosed in membrane. As they also do not possess multicellular body design, these characters bring them closer to Monera and exclude them from the kingdom Plantae.
Q14. What is the difference between bilateral and radial symmetry?
Ans. An animal is said to have bilateral symmetry if it has two equal but opposite right and left halves when cut lengthwise in the middle vertical plane, e.g., frog. On the other hand, an animal is said to have radial symmetry, if it is symmetrical with respect to any plane passing through its longitudinal axis. In other words, any plane passing longitudinally through any diameter divides the body into equal halves, e.g., Hydra.
Q15. How is notochord different from nerve cord?
Ans. Notochord is the skeletal rod which lies lengthwise between the central nervous system and the alimentary canal or the gut and the chordates possess it at young stage of development. In adult vertebrates, it is replaced by vertebral column. On the other hand, a nerve cord is a solid strand of nervous tissue, forming part of central nervous system, especially of invertebrates. The main difference between the two is that notochord is a part of skeleton system whereas nerve cord is a part of nervous system.
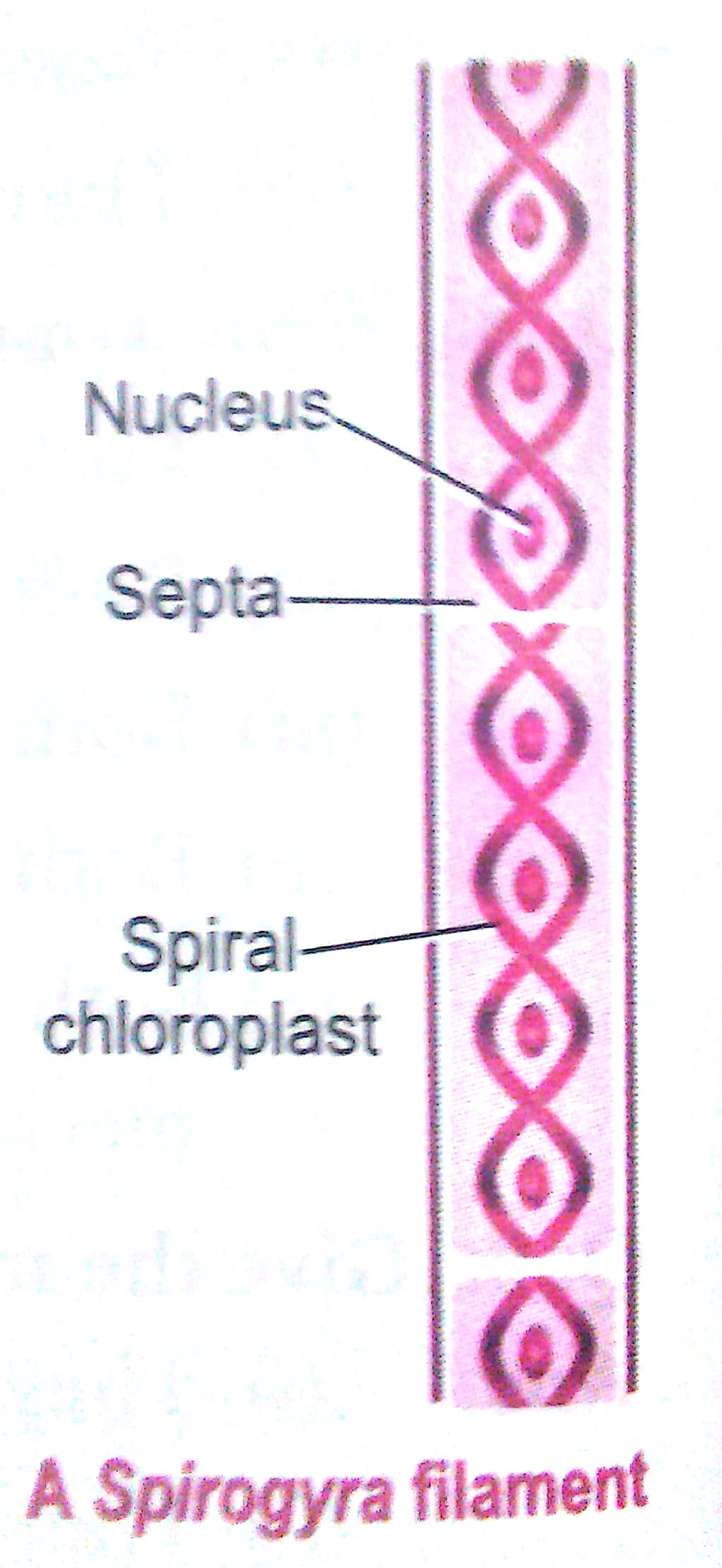
Q16. Write names of few thallophytes. Draw a labelled diagram of Spirogyra.
Ans. Ulothrix, Spirogyra, Cladophora, Ulva and Chara are few thallophytes.
Q17. Define the terms and give one example of each.
(i) Coelom (ii) Triploblastic
Ans.
(i) Coelom is the internal body cavity between visceral organs and body wall in which well developed organs can be accommodated, eg., in butterfly.
(ii) Animals having three layers of cells from which differentiated tissue can be made are called triploblastic, e.g., star fish.
Q18. You are siven leech, Nereis, Scolependra, prawn and scorpion and all have segmented body organisms. Will you classify them in one group? If no, give the important characters based on which you will separate these organisms into different groups.
Ans. All organisms give in the question do not belong to same group. Leech and Nereis belong to phylum annelida because they have metamerically segmented body, i.e., body is divided into many segments internally by septa. Body segmewnts are lined up one after the other from head to tail. But Scolopendra, prawn and scorpion belong to phylum arthropoda as these have jointed legs and open circulatory sustem.
Q19. Classify the following organisms based on the absence/presence of true coelom (i.e., acoelomate, pseudocoelomate and coelomate):
Spongilla, Sea anemone, Planaria, Liver fluke, Wuchereria, Ascaris, Nereis, Earthworm, Scorpion,
Ans.
Spongilla – Acoelomate Sea anemone – Acoelomate
Planaria – Acoelomate Liver fluke – Acoelomate
Wuchereria – Pseudocoelomate Ascaris – Pseudocoelomate
Nereis – Coelomate Scorpion – Coelomate
Earthworm – Coelomate Birds, Fishes and Horse - Coelomate.
Q. 20. Fill in the boxes given in figure with appropriate characteristics/plant group(s).
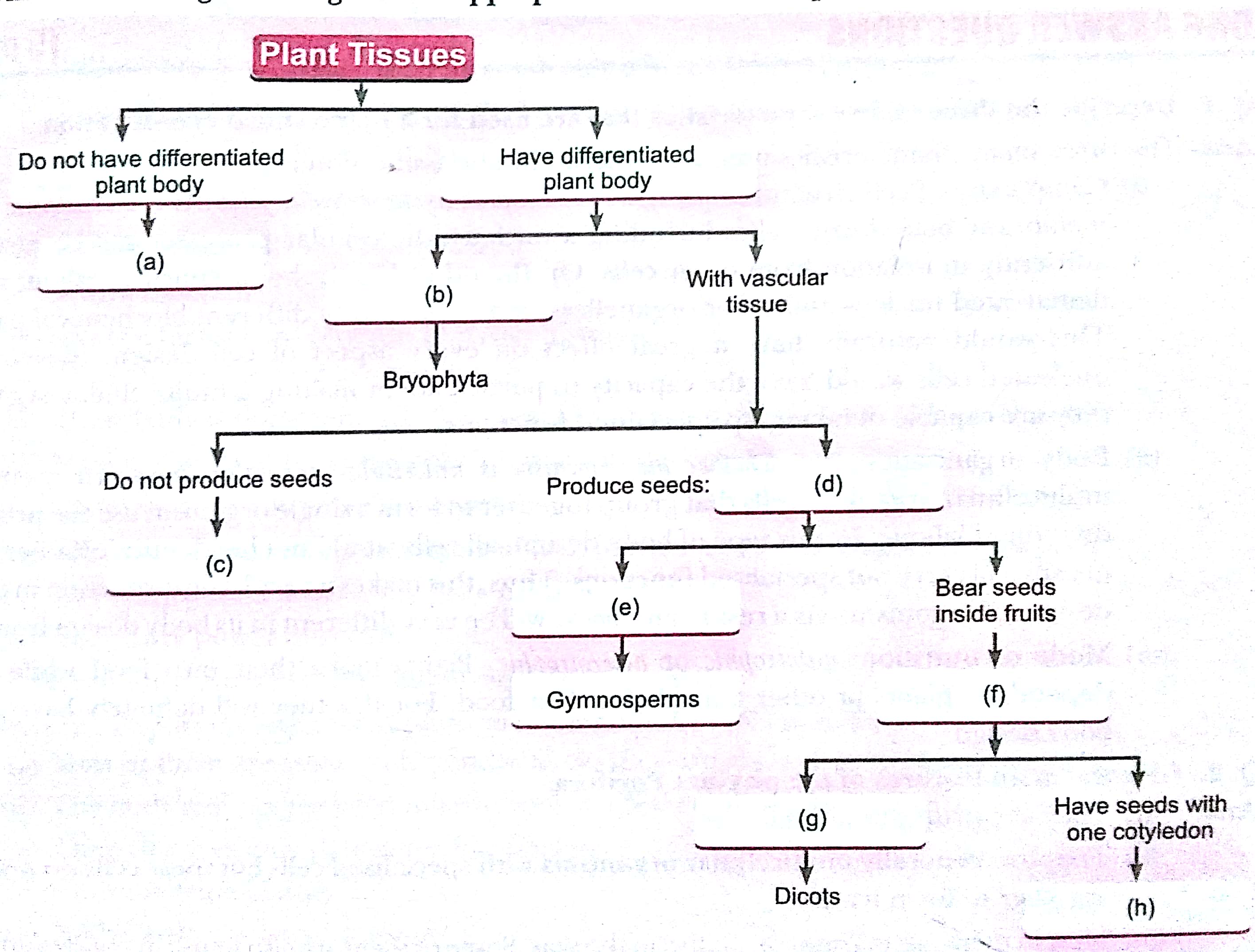
Ans.
(a) Thallophyta (b) Without specialised vascular tissue
(c) Pteridophyta (d) Phanerogams
(e) Bear naked seeds (f) Angiosperms
(g) Have seeds with two cotyledons (h) Monocots
Q.21. Label a, b, c and d given in figure. Give the function of part (b).
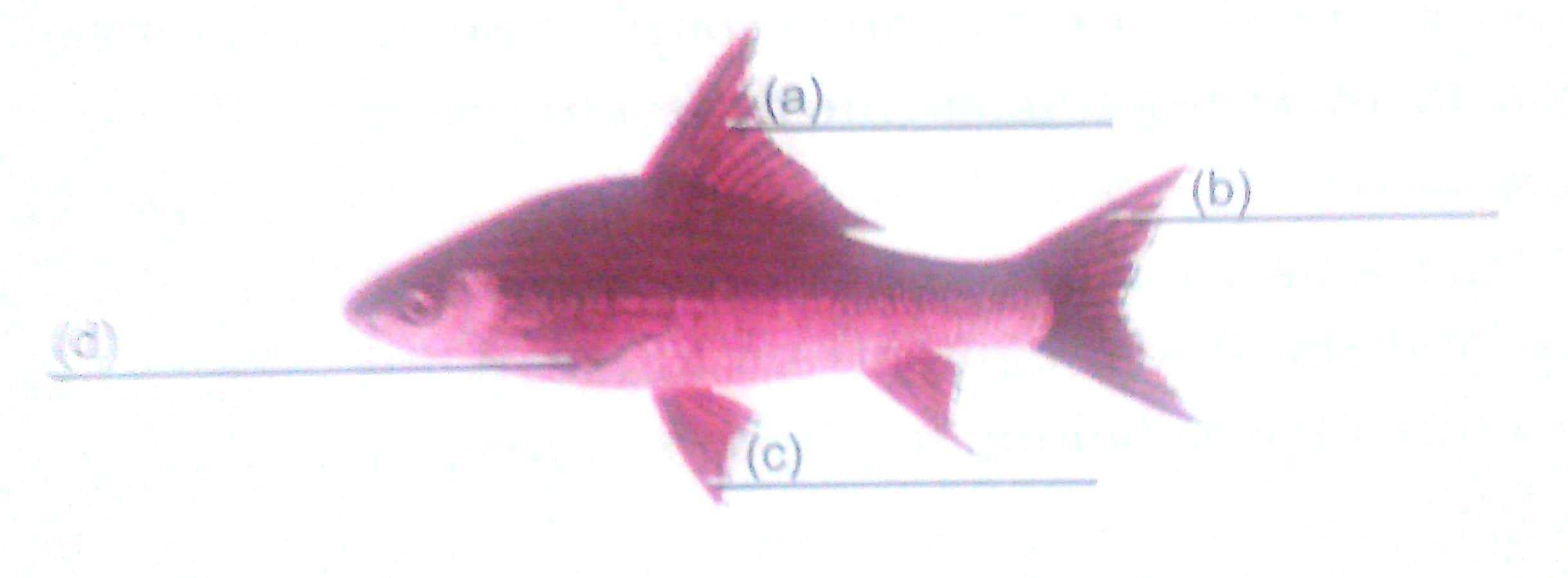
Ans.
(a) Dorsal fin (b) Caudal fin
(c) Pelvic fin (d) Pectoral fin
Function of caudal fin: Caudal fin helps in streamlined movement in water.
Q.22. List out some common features in cat, rat and bat.
Ans. Bat, rat and cat belong to the class mammalia and all have following common features:
(i) have notochord at some stage of life cycle.
(ii) are warm-blooded.
(iii) have four-chambered heart.
(iv) have skin covered with hair and sweat and oil glands.

