Short Answer Questions - II - 3 Marks
Que 1. Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances with the help of one example each. List two changes in habit that people must adopt to dispose non-biodegradable waste, for saving the environment.
Ans.
|
S.NO. |
Biodegradable wastes |
Non-biodegradable wastes |
|
(i)
(ii) |
Waste materials which can be broken down into harmless substances in nature in due course of time by the action of microorganisms such as certain bacteria are called biodegradable wastes.
Examples: Cattle dung, wool, paper, compost. |
Waste materials which cannot be broken down into harmless substances by the action of microorganisms in nature are called non-biodegradable wastes.
Examples: Plastics, polythene bags, metal articles, glass objects. |
People should adopt following changes in habit:
(a) Dispose household waste, chemical waste and hospital waste in a landfill
(b) Broken plastic articles such as buckets, bowls, cups, plates, etc., should be sent to plastic processing factories.
Que 2. Give reason to justify the following:
(a) The existence of decomposers is essential in a biosphere.
(b) Flow of energy in a food chain is unidirectional.
Ans. (a) The existence of decomposers is essential in a biosphere because they breakdown complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances that can be absorbed by the plants. Thus, decomposers:
(i) replenish the soil naturally
(ii) helps in removing the biodegradable waste.
(b) In a food chain the energy moves progressively through the various trophic levels, it is no longer available to the previous level (
Hence, the flow of energy is unidirectional.
Que 3. What is biodiversity? What will happen if biodiversity of an area is not preserved? Mention one effect of it.
Ans. The variety of life forms found in a particular region forms its biodiversity.
If biodiversity of an area is not preserved, it will result in
(i) natural calamities such as floods, forest fires and hurricanes.
(ii) soil erosion and desertification because of deforestation.
(iii) large-scale habitat losses and extinction of vulnerable animal and plant species.
(iv) sudden climatic changes and instability in the functioning of the ecosystem.
The effect of biodiversity loss would be disturbance of ecosystem balance.
Que 4. What is an ecosystem? List its two main components. We do not clean natural ponds or lakes but an aquarium needs to be cleaned regularly. Why is it so? Explain.
Ans. An ecosystem is defined as a dynamic system of biotic and abiotic components and there is a continuous flow of energy between the different components.
Its two main components are:
(i) Biotic component/living organisms
(ii) Abiotic component/physical factors
An aquarium needs to be cleaned regularly because it is an artificial and incomplete ecosystem in which natural decomposers are absent and the water is stagnant. Thus, water do not clean itself in an aquarium.
Que 5. "Energy flow in food chains is always unidirectional." Justify this statement. Explain how the pesticides enter a food chain and subsequently get into our body.
Ans. In a food chain the energy moves progressively through the various trophic levels and is no longer available to the organisms of the previous trophic level. The energy captured by the autotrophs does not revert back to the solar input. Thus, energy flow in food chains are said to be unidirectional.
Pesticides used for crop protection when washed away go down into the soil. These pesticides absorbed by plants which are the producers. On consumption of these plants, the pesticides enter our food chain and being non-biodegradable, these chemicals get accumulated progressively and enter our body.
Que 6. Give two differences between food chain and food web.
Ans.
|
Food Chain |
Food Web |
|
1. Food chain is a series of organisms feeding on one another. 2. Members of higher trophic level feed upon a single type of organism of the lower trophic level. |
1. Food web consists of a number of interlinked food chains. 2. Members of higher trophic level can feed upon organisms of the lower trophic levels of other food chain. |
Que 7. Why does vegetarian habit help us in getting more energy? In terms of energy who is at an advantageous position (vegetarian or a non- vegetarian)? Why?
Ans. We know that, vegetarians obtain food directly from plants while non- vegetarians get the food from animals. Animals (herbivores) contain 10% of food energy as compared to plants (producers). For example; the same amount of producer which supplies say 1000 J of food energy to a vegetarian will provide only 100 J of food energy to a non-vegetarian. Hence, a vegetarian will be at an advantageous position.
Que 8. Calculate the amount of energy available to tiger in the following food chain if plants have 30,000 J of energy available from the Sun:
Plant → Deer-→ Tiger
Ans. Plants can trap only 1% of the Sun's energy falling on them. Now, 1% of 30,000 J is 300 J which is the energy available to plants.
The plants are eaten up by deer. According to 10% law, 10% of 300 J
The deer will transfer 10% of its 30 J energy to the tiger. Thus, the food energy available to the tiger will be 10% of 30 J which is 3 J.

Que 9. Give three characteristics of food chain.
Ans. (i) A food chain is always straight and proceeds in a progressive straight line.
(ii) A food chain helps in understanding the food relationship and interactions among various organisms in an ecosystem.
(iii) It also helps to understand the movement of toxic substances in an ecosystem and the problem of their biological magnification.
Que 10. Describe any four modes of disposal of waste.
Ans. (i) Disposing of biodegradable wastes in biogas plants so that it can help in the preparation of biogas and manure.
(ii) Solid wastes should be buried in urban areas as landfills.
(iii) Some solid wastes (plastic, paper and metals) should be recycled.
(iv) Large amount of waste must be burnt at high temperature (incineration).
Que 11. What are the advantages of cloth bags over plastic bags during shopping?
Ans. Cloth bags:
(i) are capable of carrying more items.
(ii) are made of biodegradable material.
(iii) do not pollute our environment.
(iv) can be reused.
Que 12. How is ozone formed in the upper atmosphere? What causes its damage?
Ans. 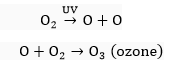
Certain harmful chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), are released into the air. These accumulate in the upper atmosphere and react with ozone resulting in reduction of the ozone layer by forming a hole. Thus, ozone layer becomes thinner and gets depleted allowing more ultraviolet rays to pass through the earth's atmosphere. These radiations are highly damaging to organisms and cause skin cancer, damage to eyes, including increased incidence of cataract and damage to immune system of human beings and other animals.

