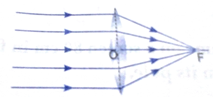
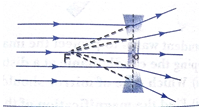
Short Answer Questions - II - 3 Marks
Que 1. Distinguish between real image and virtual image.
Ans.
|
Real Image |
Virtual Image |
|
1. It is formed by the actual meeting of reflected (Or refracted) rays.
3. It is always inverted. 4. It is formed by concave mirror or convex lens. |
1. It is formed when reflected (or refracted) rays appear to meet when produced backwards. 2. It cannot be obtained on the screen. 3. It is always erect. 4. It is formed by concave, convex and plane mirrors (or concave and convex lenses). |
Que 2. Study the ray diagram given below and answer the following questions:
(i) State the type of lens used in the figure.
(ii) List two properties of the image formed
(iii) In which position of the object will the margination be - 1?
Ans. (i) Convex lens.
(ii) Real, inverted, enlarged.
(iii) When object is at 2F.
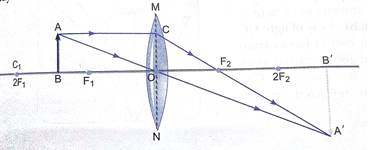
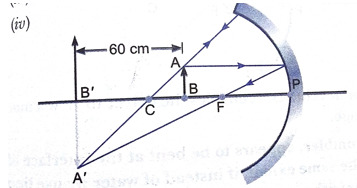
Que 3. To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of lights which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these ray after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rats find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
Ans. The candidate may choose the following rays:
(i) A ray parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus of a concave mirror.
(ii) A ray passing through the center of curvature of a concave mirror after reflection is reflected back along the same path.
Object distance,
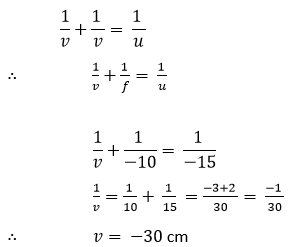
The image is foamed at a distance of 30 cm in front of mirror (negative sign means object and image are on the same side). It is real and inverted.
Que 4. Explain with the help of a ray diagram, why a pencil partly immersed in water appears to be bent at the water surface.
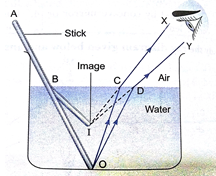
Ans. A stick or a pencil half immersed in water at an angle appears bent due to refraction of light at the air – water surface. Figure shows a straight stick AO whose lower portion BO is immersed in water. It appears to be bent at point B in the direction BI. A ray of light OC coming from the lower end O passes from water into air at C and get refracted away from the normal in the direction CX. Another ray OD get refracted in the direction DY. The two refracted ray CX and DY, when produced backward, appear to meet at point I, nearer to the water surface then O. Similar each part of the immersed portion of the stick raised As a result immersed portion of the stick raised As a result immersed portion of the stick appears to be bent when viewed at an angel from outside.
Que 5. Draw a ray diagram to show the part of the reflected ray in each of the following cases. A ray of light incident in a convex mirror
(a) Strikes at its pole marking an angle  from the principal axis.
from the principal axis.
(b) Is directed towards its principal focus.
(c) is parallel to its principal axis.
Ans.
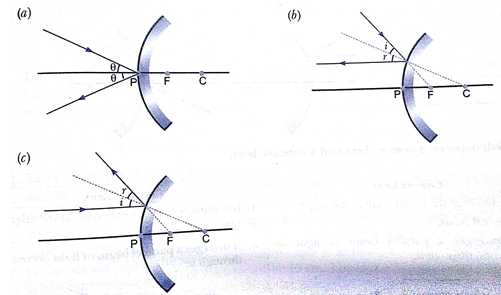
Que 6. A student want to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 80 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the candle flame at a distance of 20 cm from its pole.
(i) Which type of mirror should the student use?
(ii) Find the magnification of the image produced.
(iii) Find the distance between the object and its image.
(iv) Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case and mark the distance between the object and its image.
Ans. (i) concave mirror should be used.
(ii) Object distance,
Magnification, m = ?
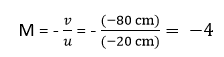
(iii) Distance between object and its image =
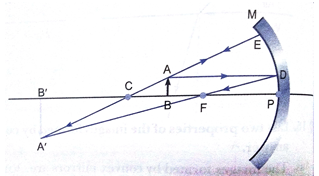
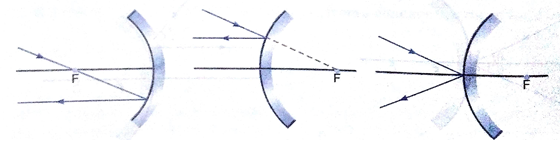
Que 7. Draw the following diagram, in which a ray of light is incident on a concave/convex mirror, on your answer sheet. Show the part of this ray, after reflection, in each case. 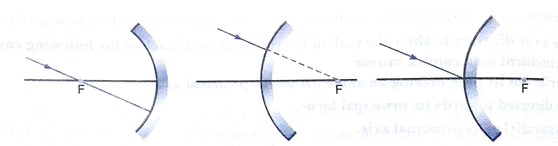
Ans.
Que 8. Distinguish between a convex lens and a concave lens.
Ans.
|
Convex Lens |
Concave Lens |
|
1. It is thicker at the Centre than at the edges. 2. It has real focus. 3. It converges a parallel beam of light on reification through it.
|
1. It is thinner at the Centre than at the edges. 2. It has virtual focus. 3. It diverges a parallel beam on refraction through it. |
Que 9. If the image fumed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
Where and why do we generally use this type pf mirror?
Ans. A convex mirror always produces an erect and diminished image of the object placed in front of it irrespective of the position of the object.
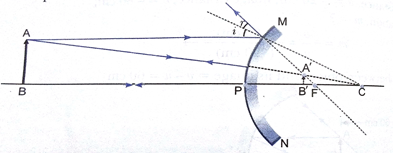
A convex mirror is used as a rear view mirror in vehicles. It enables the driver to view a much larger area of the traffic behind. It forms erect image.
Que 10. A pencil when dipped in water in a glass tumbler, appears to be bent at the interface of air and water. Will the pencil appear to bend to the same extent, if instead of water we use liquids like, kerosene or turpentine. Support your answer with reason.
Ans. No. Bending will be different in different liquids since velocity of light at the interface separating two media depends on the relative refractive index of the medium. A substance having higher refractive index is optically denser than another substance having lower refractive index. Thus higher the refractive index of a substance, more it will change the direction of a beam of light passing through it.
Que 11. How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light? Obtain an expression for refractive index of a medium with respect in teams of speed of light in these two media?
Ans. The refractive index of the media
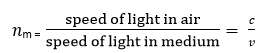
Let
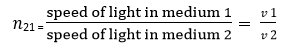
Que 12. Sudha finds out that the sharp image of the window pane of her science laboratory is foamed a distance of 15 cm from the lens. She now tries to focus the building visible to her outside the window intend of the window pane without disturbing the kens, in which direction will she move the screen to obtain a sharp image of the building? What is the approximate focal length of this lens?
Ans. Sudha should move the screen towards the lens so as to obtain a clear image of the building. The approximate focal length of this lens will be 15 cm. The rats of light coming from distant object such as a tree (or a distant building or electricity pole) can be considered to be parallel to each other. When parallel rays of fight are incident on a convex lens, the after refraction, convection at focus on the other side of the lens.