Short Answer Questions - II - 3 Marks
Que 1. Write the main aim of classifying elements. Name the basic property of elements used in the development of Modern Periodic Table. State the Modern Periodic Law. On which side (part) of the Modern Periodic Table do you find metals, metalloids and non-metals?
Ans. Elements are classified for systematic and simplified study of elements and their compounds. The basic property of elements used in the Modern Periodic Table is the atomic number of the elements. Modern Periodic Law states that "the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number."
metals are found on the left side and centre of the Modern Periodic Table.
Non-metals are found on the right side of the Modern Periodic Table.
Metalloids are found in zig-zag manner between the metals and the non-metals.
Que 2. How many groups and periods are there in the Modern Periodic Table? How do the atomic size and metallic character of elements vary as we move:
(a) down a group and
(b) from left to right in a period
Ans. There are 18 groups and 7 periods in the Modern Periodic Table.
(a) Atomic size increases
Metallic character increases
(b) Atomic size decreases
Metallic character decreases
Que 3. From the following elements:
4Be; 9F; 19K; 20Ca
(i) select the element having one electron in the outermost shell.
(ii) Two elements of the same group.
Write the formula and mention the nature the compound formed by the union of 19K and element X (2,8,7).
Ans.
|
Element |
Electronic configuration |
|
Be F K Ca |
2,2 2,7 2,8,8,1 2,8,8,2 |
(i) K
(ii) Be and Ca as both have same number of valence electrons, i.e., 2.
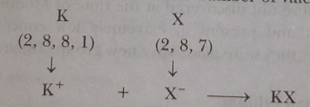
Ionic or electrovalent bond is formed.
Que 4. Name any two elements of group one and write their electronic configurations. What similarity do you observe in their electronic configurations? Write the formula of oxide of any of the aforesaid element.
Ans. Two elements of group I are Sodium (Na) and potassium (k).
Their electronic configurations: Na = 2,8,1; K = 2,8,8,1
Similarity: Both have one valence electron.
Formula of their oxides: Na2O; K2O.
Que 5. Write the number of periods the Modern Periodic Table has. State the changes in valency and metallic character of elements as we move from left to right in a period. Also state the changes, if any, in the valency and atomic size of elements as we move down a group.
Ans. The Modern Periodic Table has 7 periods. Valency across a period increases from 1 to 4, then decreases from 4 to zero.
Metallic character of elements across a period decreases.
Valency down a group remains the same. Atomic size of elements down a group increases.
Que 6. The elements 4Be, 12Mg and 20Ca, each having two valence electrons in their valence shells are in periods 2, 3 and 4 respectively of the Modern Periodic Table. Answer the following questions associated with these elements, giving reason in each case:
(a) In which group should they be?
(b) Which one of them is least reactive?
(c) Which one of them has the largest atomic size?
Ans. (a) In group 2, as each element has two valence electrons.
(b) Be is least reactive because Be has the least tendency to lose electrons.
(c) Ca has the largest atomic size as Ca has the maximum number of shells and atomic size increases down the group.
Que 7. Given below are some elements of the Modern Periodic Table. Atomic number of the element given in the parentheses:
A(4), B(9), C(14), D(19), E(20)
(a) Select the element that has one electron in the outermost shell. Also write the electronic configuration of this element.
(b) Which two elements amongst these belong to the same group? Give reason for your answer.
(c) Which two elements amongst these belong to the same period? Which one of the two has bigger atomic radius?
Ans. (a) D; the electronic configuration of D(19) is 2, 8,8, 1.
(b) A and E belong to the same group as both have the same number of valence electrons, i.e., 2.
(c) A, B and D, E.
A has a bigger atomic radius than B and D has a bigger atomic radius than E.
Que 8. Nitrogen (atomic no. 7) and phosphorous (atomic no. 15) belong to group 15 of the Periodic Table. Write the electronic configuration of these two elements in terms of K, L, M, N shell. Predict whether these are metallic or non-metallic.
Ans.
|
Element |
K |
L |
M |
|
N (7) P (15) |
2 2 |
5 8 |
|
Both are non-metals as they tend to form bonds by gaining electrons.
Que 9. Na, Mg and Al are the elements of the same period of Modern Periodic Table having one, two and three valence electrons respectively. Which of these elements (i) has the largest atomic radius, (ii) is least reactive? Justify your answer stating reason for each case.
Ans. (i) Na has the largest atomic size because the atomic size decreases from left to right due to the increase in the nuclear charge.
(ii) Al is least reactive because the tendency to lose electrons decreases from left to right.
Que 10. Two elements 'P' and 'Q’ belong to the same period of the Modern Periodic Table and are in Group-1 and Group-2 respectively. Compare their following characteristics in tabular form:
(a) The number of electrons in their atoms
(b) The sizes of their atoms
(c) Their metallic characters
(d) Their tendencies to lose electrons
(e) The formula of their oxides
(f) The formula of their chlorides
Ans.
|
Characteristic |
P |
Q |
|
(a) Number of electrons in their atoms (b) Side of their atoms (c) Metallic character (d) Tendencies to lose electrons (e) Formula of their oxides (f) Formula of their chlorides |
P is more metallic than Q. P will lose electrons more easily. P2P |
Number of electrons is more. Q is smaller in size. Q is less metallic Q does not lose electrons easily. QO |
Que 11. The position of three elements A, B and C in the periodic Table is shown below:
|
Groups → |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
1 |
||||||||
|
2 |
B |
|||||||
|
3 |
A |
C |
Giving reasons, explain the following:
(i) Element A is a metal.
(ii) Element C has larger size than element B.
(iii) Elements B has a valency of 3.
Ans. (i) Element A belongs to group 1 of the Periodic Table. So, it has 1 valence electron and it forms unipositive ion by losing its valence electron. Hence, A is a metal.
(ii) This is because element C is in third period while element B is in second period. We know that the atomic size increases down the group and decreases along a period.
(iii) Element B is in 2nd period and 3rd group hence it has 3 valence electrons. It loses 3 electrons to achieve nearest inert gas configuration. So, its valency is 3.
Que 12. Identify the elements with the following property and arrange them in increasing order of their reactivity.
(a) An element which is a soft and reactive metal.
(b) The metal which is an important constituent of limestone.
(c) The metal which exists in liquid state at room temperature.
Ans. (a) Na or K (b) Ca (c) Hg
Reactivity order: Hg < Ca < Na <K
Que 13. Properties of the elements are given below. Where would you locate the following elements in the Periodic Table?
(a) A soft metal stored under kerosene.
(b) An element with variable (more than one) valency stored under water.
(c) An element which is tetravalent and forms the basis of organic chemistry.
(d) An element which is an inert gas with atomic number 2.
(e) An element whose thin oxide layer is used to make other elements corrosion resistant by the process of"anodising".
Ans. (a) Sodium (Na) Group 1 and Period 3 or Potassium (K) Group I and Period 4
(b) Phosphorus (P) Group 15 and Period 3
(c) Carbon (C) Group 14 and Period 2
(d) Helium (He) Group 18 and period 1
(e) Aluminium (Al) Group 13 and Period 3
Que 14 The atomic number of an element 'X' is 20.
(i) Determine the position of the element 'X' in the periodic table.
(ii) Write the formula of the compound formed when ‘X' reacts/combines with another element 'Y' (atomic number 8).
(iii) What would be the nature (acidic or basic) of the compound formed? Justify your answer.
Ans. Electronic configuration: 2, 8, 8, 2
(i) 'X' is in the 2nd group and 4th period of the periodic table.
(ii) X + Y → XY
2,8,8,2 2,6
(iii) The nature of the compound formed is basic because X is a metal and Y is oxygen. The oxides of metals are basic in nature.
Que 15. The following table shows the position of six elements A, B, C, D, E and F in the Periodic Table.
|
Groups→ |
1 |
2 |
3 to 12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
|
2. |
A |
B |
C |
||||||
|
3. |
D |
E |
F |
Using the above table answer the following questions:
(a) Which element will form only covalent compounds?
(b) Which element is a metal with valency 2?
(c) Which element is a non-metal with valency 3?
(d) Write a common name for the family of elements C and F
(e) Out of D and E, which one has a bigger atomic radius and why?
Ans. (a) E
(b) D
(c) B
(d) The noble gases.
(e) D has bigger atomic radius. The atomic radius decreases in moving from left to right along a period. This is due to an increase in nuclear charge which tends to pull the electrons closer to the nucleus and reduces the size of the atom.
Que 16. The atomic radii of first group elements of the Periodic Table are as follows:
|
Group 1 elements |
Na |
Li |
Rb |
Cs |
K |
|
Atomic radius (Pm) |
186 |
152 |
244 |
262 |
231 |
(i) Arrange these elements in the increasing order of their atomic radii.
(ii) Name the elements which have the smallest and the largest atoms.
(ii) How does the atomic size vary as you go down a group?
Ans. (i)
|
Group 1 elements |
Li |
Na |
K |
Rb |
Cs |
|
Atomic radius (Pm) |
152 |
186 |
231 |
244 |
26 |
(ii) The elements Li has the smallest atom (atomic radius 152 Pm) whereas the elements Cs has the largest atom (atomic radius 262 Pm).
(iii) From this arrangement, we find that the atomic size (or radius) increase down the group.
Que 17. The elements of the second period of the Periodic Table are given below:
Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F
(i) Explain why atomic radius decreases from Li to F.
(ii) Identify the most metallic and non-metallic elements among the above elements.
Ans. (i) On moving from left to right along a period of the Periodic Table, atomic number increases, i.е., number of protons and electrons increases which ultimately increases the nuclear charge.
Hence, the electrons are pulled in closer to the nucleus which leads to contraction of the atom and thus atomic radius is decreased.
(ii) On moving from left to right in a Periodic Table, metallic character decreases and non-metallic character increases. This is because the capacity to lose electrons from outermost orbit of an atom (called ionisation energy) decreases. Hence, among the above elements Li being placed on extreme left side is most metallic and F being placed on extremely right side is most non-metallic element.
Que 18. The atomic numbers of nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine are 7, 8 and 9 respectively. Write the electronic configuration of each element and answer the following questions:
(a) Which one of N, O and F is most electronegative and which one is least electronegative?
(b) What is the number of valence electrons of F?
(c) What is valency of each one of N, O and F?
Ans. Electronic configuration of
Nitrogen : 2, 5
Oxygen : 2 ,6
Fluorine : 2, 7
(a) Fluorine (F) is most electronegative and nitrogen (N) is least electronegative.
(b) Fluorine (F) has 7 valence electrons.
(c) Valency of nitrogen is 3 and 5, valency of oxygen is 2, valency of fluorine is 1.
Que 19. Four elements P, Q, R and S belong to the third period of the Modern Periodic Table and have respectively 1,3, 5 and 7 electrons in their outermost shells. Write the electronic configurations of Q and R and determine their valencies. Write the molecular formula of the compound formed when P and S combine.
Ans. Electronic configuration of Q : 2, 8,3
Valency of Q : 3
Electronic configuration of R : 2, 8, 5
Valency of R: 8 - 5 = 3
P + S → PS
2, 8 ,1 2, 8, 7
Que 20. Consider the following elements:
Li, Cl, Br, Na, K, I
(i) Arrange the elements according to the groups to which they belong in the Periodic Table.
(ii) What are the common properties on the basis of which the elements have been grouped together?
Ans. (i) Li, Na and K are grouped together in the periodic table and belong to group I. They are grouped together necause all of them have one electron in their valence shell. Rest of the element Cl, Br and I are grouped together in the periodic table and belong to group 17.
(ii) The elements of group I are called alkali metals because they react with water to liberate H2 gas and form alkalis. The elements of group 17 are monovalent non-metals. They form acidic oxides and are called halogens.
Que 21. Atomic number is considered to be a more appropriate parameter than atomic mass for classification of elemenents in a periodic table. Why?
How does metallic character of elements vary on moving from
(i) left to right in a period?
(ii) from top to bottom in a group?
Give reasons for your answers.
Ans. The properties of elements depend upon valence electrons in the atom which in turn depends on the total number of electrons i.e., atomic number. Therefore, atomic number is a more appropriate parameter than atomic mass for classification of elements.
(i) On moving from left to right in a period, the metallic character decreases. This is due to an increase in nuclear charge which tends to pull the electrons closer to the nucleus and reduces the size of the atom.
(ii) On moving from top to bottom. in a group, metallic character increases. This is because new shells are being added as we go down the group. This increases the distance between the valence shell and the nucleus.
Que 22. Two elements with symbol X (atomic no. 16) and Y (atomic no. 12) are placed in the III period of the Modern Periodic Table.
(i) Which amongst the two has more metallic character
(ii) Calculate the valency of each element.
(iii) Element 'Y' is smaller than 'X' in terms of atomic size. Is the statement true, justify?
Ans. (i) Y
(ii) 2 each
(iii) False, same period but Y lies in group 2 and X in group 16. So, as we move from left to right size decreases with increase in nuclear charge.
Que 23. Taking the example of an element of atomic number 16, explain how the electronic configuration of the atom of an element relates to its position in the Modern Periodic Table and how valency of an element is calculated on the basis of its atomic number.
Ans. Atomic number of the element = 16
Electronic configuration 2, 8, 6
Period number Number of shells
The atom of the element has three shells. So, the period number is 3.
The atom of the element has six valence electrons. So, the group number of the element will be 16 (6+ 10).
Valency 8-number of valence electrons (> 5) or number of valence electrons (< 5)
Que 24. Calcium is an element with atomic number 20. Stating reason answer each of the following questions:
(i) Is calcium a metal or non-metal?
(ii) Will its atomic radius be larger or smaller than that of potassium with atomic number 19?
(iii) Write the formula of its oxide
Ans. (i) Calcium is a metal since it has two electrons in its outermost shell which it can lose easily.
(ii) K (19) is placed before Ca(20) in the same period (fourth period). Since the atomic radius decreases along a period, the atomic radius of calcium is smaller than that of potassium.
(iii) The formula of oxide of calcium is CaO, because the valency of calcium as well as that of oxygen is 2.

