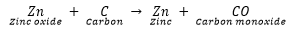Short Answer Questions - II - 3 Marks
Que 1. Name two metals which react violently with cold water. Write any observation you would make when such a metal is dropped into water. How would you identify the gas evolved, if any, during the reactions?
Ans. Metals which react violently with cold water are potassium (K) and sodium (Na).
2K + 2H2O
2Na + 2H2O
The hydrogen gas produced during the reaction of these tow metals with water immediately catches fire. Thus, these reactions are violent and exothermic.
The gas evolved during these reaction burns with popping sound which confirms that the gas is hydrogen (H2).
Que 2. Give reasons:
(i) Reactivity of Al decreases if it is dipped in HNO3.
(ii) Carbon cannot reduce the oxides of Na or Mg.
(iii) NaCl is not a conductor of electricity in solid state whereas it does conduct electricity in aqueous solution as well as in molten state.
(iv) Metals like Na, K, Ca and Mg are never found in their free in nature.
Ans. (i) Due to the formation of a layer of oxide, i.e., Al2O3 it becomes less reactive.
(ii) Na or Mg are more reactive metals as compared to carbon. So, their oxides are more stable.
(iii) In solid NaCl, the movement of ions is not possible due to its rigid structure but in aqueous solution or molten state, the ions can move freely. These free ions are responsible for conduction of electricity.
(iv) Na, K, Ca and Mg are highly reactive metals and thus never found in their free state in nature.
Que 3. Explain the following statement:
(i) Most metal oxides are insoluble in water but some of these dissolve in water. What are these oxides and their solutions in water called?
(ii) At ordinary temperature, the surface of metal such as magnesium, aluminium and zinc, etc. is covered with a thin layer. What is the composition of this layer? State its importance.
(iii) Some alkali metals can be cut with a knife.
Ans. (i) These oxides are called basic oxides and their solutions in water are called alkalis.
(ii) This layer formed is protective oxides layer which prevents the metal from further oxidation.
(iii) Some alkali can be cut with a knife because they are very soft and have low densities.
Que 4. When a metal X is treated with cold water, it gives a basic salt Y with molecular formula XOH (molecular mass = 40) liberates a gas Z which easily catches fire. Identify X,Y and Z and also write the reaction involved.
Ans. Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) react with cold water to form basic salt NaOH and KOH respectively. The molecular mass of NaOH is 40. So, X is Na and Y is NaOH. The gas liberated during the reaction is hydrogen (H2). So. Z is H2.
2Na + 2H2O  2NaOH + H2 + Heat energy
2NaOH + H2 + Heat energy
Que 5. Of the three metals X,Y and Z,X reacts with cold water,Y with hot water and Z with steam only. Identify X,Y and Z and also arrange them in order of increasing reactivity.
Ans. X is an alkali metal, Na or K.
Y is an alkaline earth, Mg or Ca.
Z is Fe.
Increasing reactivity series: Na > Mg > Fe.
Que 6. An element A burns with golden flame in air. It reacts with another element B, atomic number 17 to give a product C. An aqueous solution of product C on electrolysis gives a compound D and liberates hydrogen. Identify A , B, C and D. Also write down the equations for the reactions involved.
Ans. A – Na; B – Cl2; C – NaCl; D - NaOH
2Na + Cl2
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Que 7. Iqbal treated a lustrous, divalent element M with sodium hydroxide. He observed he formation of bubbles in reaction mixture. He made the same observation when this element was treated with hydrochloric acid. Suggest how can he identify the produced gas. Write chemical equations for both the reactions.
Ans. The element is a metal.
M + 2NaOH
M + 2HCl
Que 8. Give reason:
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, Potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yetit is used to make utensils for cooking.
Ans. (a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery because of their bright shiny surface and high resistance to corrosion. Also they have high malleability and ductility.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil to prevent their reaction with oxygen, moisture and carbon dioxide of air so as protect them as they are highly reactive metals.
(c) Aluminium metal forms a thin layer of aluminium oxide all over its surface under the action of moist air. This layer prevents the metal underneath from further corrosion. It is cheap, easily available, malleable and ductile. Therefore, it is used to make utensils for cooking.
Que 9. Give the differences between electrolytic reduction and reduction with carbon.
Ans.
|
Reduction with carbon |
Electrolytic reduction |
|
1. Carbon is used as a reducing agent. 2. Oxides of moderately reactive metals (e.g., Zn, Fe, Cu, Ni) are reduced by carbon.
|
2. Oxides (and chlorides) of highly reactive metals (e.g., Al, Na, K, Mg, Ca) are reduced by this process. 3. In this process, molten metal oxide is electrolysed in an electrolytic cell where the cathode acts as a powerful reducing agent by supplying electrons to reduce metal ions into metal.
|
Que 10. What is meant by refining of metals? Describe the electrolytic refining of copper with a neat labelled diagram.
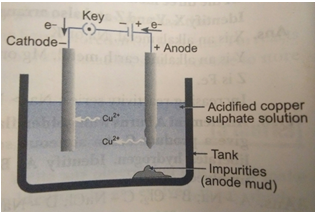
Ans. In electrolytic refining process, the impure metal is made as anode and a thin strip of pure metal is made as cathode. A solution of the metal salt is made as an electrolyte. On passing the current through the electrolyte, the pure metal from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte. An equivalent amount or pure metal from the electrolyte is deposited on the cathode. The soluble impurities go into the solution, whereas, the insoluble impurities settle down at the bottom of the anode and are known as anode mud.
At anode: Cu
At cathode: Cu2+ + 2e-
Que 11. An ore on heating in air produces sulphur dioxide. Which process would you suggest for its concentration? Describe briefly any two steps involved in the conversion of this concentrated ore into related metal.
Ans. The ore on heating produces sulphur dioxide gas so it is a sulphide ore. The method used for its concentration is “froth floatation process”. After concentration of the ore following two steps would be followed.to convert it into metal.
(i) Roasting: The sulphide ore is converted into its oxide by heating it in the presence of air.
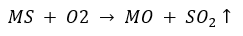
(ii) Reduction of metal oxide to metal: The oxide formed by roasting is then reduced to metal by using a suitable reducing agent like carbon (Coke).
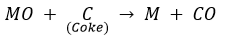
Que 12. During extraction of metal, electrolytic refining is used to obtain pure metals.
(i) Which material will be used as anode and cathode for refining of silver metal by this process?
(ii) Suggest a suitable electrolyte also.
(iii) In this electrolytic cell, where do we get pure silver after passing electric current?
Ans. (i) Anode: Impure silver
Cathode: Pure silver
(ii) Electrolyte: Silver salt, such as AgNO3, AgCl, etc.
(iii) We get pure silver at cathode.
Que 13. A metal that exists as a liquid at room temperature is obtained by heating its sulphide in the presence of air. Identify the metal and its ore and give the reaction involved.
Ans. Metal low in activity series can be obtained by reducing their sulphides or oxides by heating. Mercury is the only metal that exists as liquid at room temperature. It can be obtained by heating cinnabar (HgS), the sulphide ore of mercury.
The reaction are as follows:
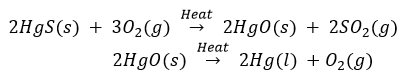
Que 14. How can a layer of aluminium oxide on an aluminium object be made thicker? What is this process called?
Ans. Aluminium develops a thin oxide layer when exposed to air. This aluminium oxide coat makes it resistant to further corrosion. The resistance can be improved further by making the oxide layer thicker. This process is called anodising.
During anodising, a clean aluminium article is made the anode and is electrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid. The oxygen gas evolved at the anode reacts with aluminium articles an attractive finish.
Que 15. (i) A metal M is found in nature as MCO3. It is used in galvanising iron articles. Name the metal.
(ii) How can the metal be obtained from its carbonate ore?
Ans. (i) The metal is zinc (Zn).
(ii) The carbonate ore is first heated strongly in limited supply of oxygen and changed into its oxide. This process is called calcination.
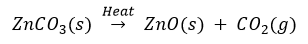
Zinc oxide is then reduced to zinc metal by heating it with carbon. This process is called reduction.
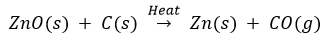
Que 16. Which two metals do not corrode easily? Give example in each case to support that
(i) Corrosion of some metals is an advantage.
(ii) Corrosion of some metals is a serious problem.
Ans. Gold and platinum.
(i) A thin impervious layer aluminium oxide forms a protective layer which protects the aluminium metals underneath from further damage.
(ii) Corrosion of iron is a serious problem. Every year enormous amount of money is spent to replace damaged iron and steel structures.
Que 17. In the formation of the compound XY, atoms of X lost one electron each while atoms of Y gained one electron each. What is the nature of bond in XY? Predict the two properties of XY.
Ans. The atoms of X electrons whereas the atoms of Y gain electrons. Thus, there is transfer of electrons from atoms of X to atoms of Y. The bond formed by the transfer of electrons is called ionic bond. Therefore, the nature of bond in the compound XY is ionic.
Properties of ionic compound XY:
(i) The compound will be soluble in water.
(ii) The compound will conduct electricity when dissolved in water or in molten state.
Que 18. Explain how the properties of an alloy are different from those of constituent metals.
Ans. (i) Alloys are stronger and harder than the constituent metals.
(ii) Alloys are more resistant to corrosion.
(iii) Alloys are more resistant to corrosion.
(iv) Alloys have lower electrical conductivity than pure metals.
Que 19. State reason for the following:
(i) Lemon is used for restoring the shine of tarnished copper vessels.
(ii) A metal sulphide is converted into its oxide to extract the metal from the sulphide ore.
(iii) Copper wires are used in electrical connections.
Ans. (i) When copper vessels are exposed to moist air, they form a green coating of basic copper carbonate [CuCO3.Cu (OH) 2].
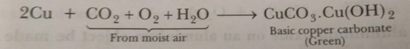
The sour substance such as lemon or tamarind juice contain acids. Lemon juice contains citric acid and tamarind contain tartaric acid. These acids dissolve the coating of copper oxides or basic copper carbonate present on the surface of tarnished copper vessels and make them shining red-brown again.
(ii) It is easier to obtain a metal from its oxides as compared to its sulphides and carbonates. So, prior to reduction, metal carbonate and sulphides must be converted into metal oxides. A carbonate ore is converted into oxide by calcination whereas a sulphide ore is converted into oxide by roasting.
(iii) Copper wires are good conductor of electricity, so they are used in electrical connections.