Short Answer Questions - II - 3 Marks
Que 1. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and balance them:
(i) Lead nitrate reacts with sulphuric acid to form a precipitate of lead sulphate and nitric acid.
(ii) Magnesium burns in the presence of nitrogen to form magnesium nitride.
(iii) Aluminium metal strip is added in hydrochloric acid to produce aluminium chloride and hydrogen gas.
Ans. (i) Pb(NO3)2(aq) + H2SO4(aq)
(ii) 3 Mg(s) + N2g
(iii) 2AI(s) + 6HCl(aq)
Que 2. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(i) nitrogen gas is treated with hydrogen gas in the presence of a catalyst at 773 K to form ammonia gas.
(ii) Sodium hydroxide solution is treated with acetic acid to form sodium acetate and water.
(iii) Ethanol is warmed with ethanoic acid to form ethyl acetate in the presence of concentrated H2SO4.
(iv) Ethene is burnt in the presence of oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water and releases heat and light.
Ans. (i) 
(ii) NaOH(aq) + CH3COOH(aq)
Double displaced reaction/Neutralisation reaction
(iii) 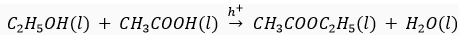
Double displaced reaction/Esterification reaction
(iv) C2H4(g) + 3O2(g)
Redox reaction /Combustion reaction
Que 3. Name the type of chemical reaction represented by the following equation:
(i) CaO + H2O
(ii) 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3
(iii) 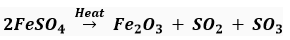
Ans. (i) Combination reaction
(ii) Double displacement reaction
(iii) Decomposition reaction
Que 4. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance the equations:
(i) Phosphorus burns in oxygen to give phosphorus pentoxide.
(ii) Aluminium metal replaces iron from ferric oxide, Fe2O3, giving aluminium oxide and iron.
(iii) Carbon disulphide burns in air to give carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide.
(iv) Barium chloride reacts with zinc sulphate to give zinc chloride and barium sulphate.
Ans. (i) P4 + 502
(ii) 2AI + Fe203
(iii) CS2 + 302
(v) BaCl2 + ZnSO4
Que 5. (i) What is observed when a solution of potassium iodide is added to a solution of lead nitrate taken in a test tube?
(ii) What type of reaction is this?
(iii) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above reaction.
Ans:
(i) A yellow precipitate of lead iodide (Pbl2) is formed.
(ii) Precipitation reaction/Double displacement reaction.
(iii) 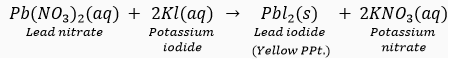
Que 6. (i) What happens when silver nitrate solution is added to sodium chloride solution? Write the equation for the reaction which takes place.
(ii) Name the type of reaction involved.
Ans. (i) When silver nitrate solution is added to sodium chloride solution, a white precipitate of silver chloride is formed along with sodium nitrate solution.
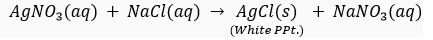
(ii) This is double displacement reaction.
Que 7. (i) What is the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this colour change after heating?
(ii) Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this change?
Ans. (i) The colour of ferrous sulphate crystals is green. On heating, FeSO4.7H2O First decomposes to form anhydrous ferrous sulphate (FeSO4) which is white in colour.
(ii) The products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals are ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide.
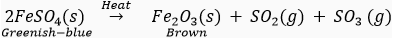
This is a type of decomposition reaction (thermal decomposition).
Que 8. Identify the oxidizing agent (oxidant) in the following reactions.
(i) Pb3O4 + 8HCL → 3PbCl2 + Cl2 + 4H2O
(ii) 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
(iii) CuSO4 + Zn → Cu + ZnSO4
(iv) V2O5 + 5Ca → 2V + 5CaO
(v) 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
(vi) CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Ans. (i) Pb3O4 (ii) O2 (iii) CuSO4
(iv) V2O5 (v) H2O (vi) CuO
Que 9. Solid calcium oxide was take in a container and water was added slowly to it,
(i) State the two observations made in the experiment.
(ii) Write the name and chemical formula of the product formed.
And. (i) Following are the two observation:
(a) Calcium oxide (CaO) reacts vigorously with water to form slaked lime.
(b) The container becomes hot because a large amount of heat is released during this reaction.
(ii) The product formed is slaked lime for lime for which the chemical formula is Ca(OH)2.
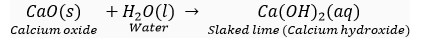
Que 10. A magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen to give a white compound X accompanied by emission of light. If the burning ribbon is now placed in an atmosphere of nitrogen, it continues to burn and forms a compound Y.
(i) Write the chemical formulae of X and Y.
(ii) Write the balanced chemical equation when X is dissolved in water.
And. 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO + Light
3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
(i) X is MgO; Y is Mg3N2
(ii) MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2
Que 11. Identify the type of chemical reaction taking place
(i) on mixing a solution of potassium chloride with silver nitrate, and insoluble white substance is formed.
(ii) on heating green coloured ferrous sulphate crystals, reddish-brown solid is left and smell of a gas having odour of burning sulphur is observed.
Ans. (i) 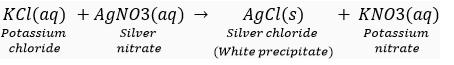
This reaction is an example of double displacement and precipitation reaction in which a precipitate of silver chloride is obtained.
(ii) 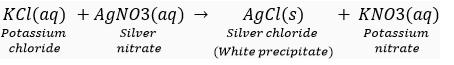
This reaction is an example of decomposition (thermal decomposition) reaction because a single substance (FeSO4) breaks down into three substances (Fe2O3, SO2 and SO3). Here, SO2 gives the smell of burning sulphur.
Que 12. Identify the type of reaction in the following examples:
(i) Na2SO4(ag) + BaCl2(aq)
(ii) Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq)
(iii) 2H2(g) + O2(g)
Ans. (i) Double displacement reaction
(ii) Displacement reaction
(iii) Combination reaction
Que 13. During the reaction of some metals with dilute hydrochloric acid, following observations were made.
(i) The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium (Al) is added.
(ii) The reaction of sodium metal is found to be highly explosive.
(iii) Some bubbles of a gas are seen when lead (Pb) is reacted with the acid.
Explain these observations giving suitable reasons.
Ans. (i) The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium is added because it is an exothermic reaction.
(ii) Reaction of sodium metal is found to be highly explosive because it is an exothermic reaction.
(iii) When lead is treated with hydrochloric acid, bubbles of hydrogen gas are evolved.
Pb(s) + 2HCl(aq)

