Short Answer Questions-II - 3 Marks
Q. 1. Identify the dispersed phase and dispersing medium in the following colloids.
(a) Fog (b) Cheese (c) Coloured gemstone
Ans.
(a) Fog-liquid, gas
(b) Cheese-liquid, solid
(c) Coloured gemstone--solid, solid
Q. 2. Describe any three properties of colloid.
Ans.
(i) It is a heterogenous mixture.
(ii) Size of particles is too small to be seen by naked eye.
(iii) They scatter light passing through them making its path visible.
(iv) They do not settle down when left undisturbed.
(v) They cannot be separated by the process of filtration. (any three points)
Q. 3. State the principle of separating two immiscible liquids by separating funnel. Describe an activity with diagram to separate a mixture of water and kerosene oil.
Ans. Immiscible layers separate out in layers depending on their densities in separating funnel.
Activity to separate kerosene oil from water using a separating funnel:
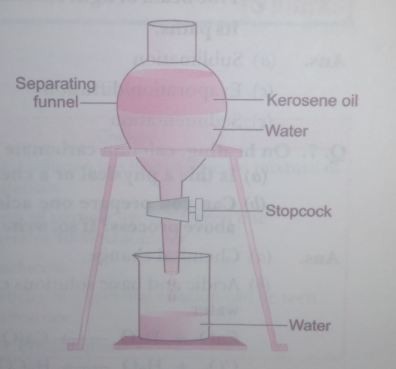
- Pour the mixture of kerosene oil and water in separating funnel as shown in figure.
- Let it stand undisturbed for sometime so that separate layers of oil and water are formed.
- Open the stopcock of the separating funnel and pour out the lower laver of water carefully.
- Close the stopcock of the separating funnel as the oil reaches the stopcock.
Q. 4. What would you observe when
(a) a saturated solution of potassium chloride prepared at 60°C is allowed to cool at room temperature?
(b) an aqueous sugar solution is heated to dryness?
(c) a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder is heated strongly?
Ans.
(a) Solid potassium chloride will separate out.
(b) Initially the water will evaporate and then sugar will get charred.
(c) Iron sulphide will be formed.
Q. 5. Suggest separation technique (s) one would need to employ to separate the following mixtures:
(a) Mercury and water
(b) Potassium chloride and ammonium chloride
(c) Common salt, water and sand
(d) Kerosene oil, water and salt.
Ans.
(a) Separation by using separating funnel
(b) Sublimation
(c) Filtration to separate sand followed by evaporation/distillation
(d) Separation by using separating funnel to separate kerosene oil followed by evaporation or distillation.
Q, 6. Name the process associated with the following:
(a) Dry ice is kept at room temperature and at one atmospheric pressure.
(b) A potassium permanganate crystal is in a beaker and water is poured into the beaker with stirring.
(c) An acetone bottle is left open and the bottle becomes empty.
(d) Milk is churned to separate cream from it.
(e) Settling of sand when a mixture of sand and water is left undisturbed for some time.
(f) Fine beam of light entering through a small hole in a dark room, illuminates the particles in its paths.
Ans.
(a) Sublimation (b) Dissolution/diffusion
(c) Evaporation/diffusion (d) Centrifugation
(e) Sedimentation (f) Scattering of light (Tyndall effect).
Q. 7. On heating, calcium carbonate gets converted into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
(a) Is this a physical or a chemical change?
(b) Can you prepare one acidic and one basic solution by using the products formed in the above process? If so, write the chemical equation involved.
Ans.
(a) Chemical change.
(b) Acidic and basic solutions can be prepared by dissolving the products of the above process in water.
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 (basic solution)
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 (acidic solution)
Q. 8. Non-metals are usually poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are non-lustrous, non-sonorous, non-malleable and are coloured.
(a)Name a lustrous non-metal.
(b) Name a non-metal which exists as a liquid at room temperature.
(c) The allotropic form of a non-metal is a good conductor of electricity. Name the allotrope.
(d) Name a non-metal which is known to form the largest number of compounds.
(e) Name a non-metal other than carbon which shows allotropy.
(f) Name a non-metal which is required for combustion.
Ans. (a) Iodine (b) Bromine
(c) Graphite (d) Carbon
(e) Sulphur (f) Oxygen
Q.9. Classify the following into metals, non-metals and metalloids:
(i) Germanium (ii) Boron
(iii) Diamond (iv) Iodine
(v) Copper (vi) Helium.
Ans. Metal - Copper
Non-metals - Diamond, iodine and helium
Metalloids - Germanium, boron.
Q. 10. Classify the following into elements, compounds and mixtures.
(i) Pure sand (ii) Air
(iii) Ammonia gas (iv) Ice
(v) Glass (vi) CaO.
Ans. Elements - Nil
Compounds - Pure sand, Ice, CaO, Ammonia gas
Mixture - Air , Glass.

