Short Answer Questions - I - 2 Marks
Que 1. What possible phenomenon can happen when light falls on a surface?
Ans. Any of the following phenomenon may happen.
(i) A portion of incident light is reflected back into the first medium.
(ii) Some portion travels through the second medium along a change path, known as refraction.
(iii) The remaining part of the light may be absorbed by the second medium.
Que 2. List two characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors?
Ans. (i) Image formed by a plane mirror is always virtual and erect.
(ii) The size of the image is equal to that of the object.
(iii) The image formed is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
(iv) The image is laterally inverted.
Que 3. List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.
Ans. (i) Virtual
(ii) Erect
(iii) Diminished
(iv) Object distance more than image distance.
Que 4. Explain the term lateral inversion.
Ans. If an word is placed in front of a plane mirror, then the right side of the object appear to be the left side of the image, and the left side of the object appear to be the right if its image. This change of sides of an object and its mirror image is called lateral inversion.
Que 5. In what way is the word AMBULANCE printed in front of the hospital vans? Why is it printed this way?
Ans. The word AMBULANCE on the hospital vans is written in the form of its mirror image as  because any vehicle which is ahead of ambulance van can see the laterally inverted alphabets correctly from his rear-view mirror and make way for it to pass through and enable it to reach the hospital quickly.
because any vehicle which is ahead of ambulance van can see the laterally inverted alphabets correctly from his rear-view mirror and make way for it to pass through and enable it to reach the hospital quickly.
Que 6. How can you distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror without touching them?
Ans. By observing the virtual images formed by the three mirrors, we can distinguish between the mirrors as:
(i) Plane mirror will produce an image of the same size,
(ii) Concave mirror will produce a magnified image, and
(iii) Convex mirror will produce a diminished image.
Que 7. State the laws of refraction of light. If the speed of light is vacuum is 3 x 108 m\s, find the absolute refractive index of a medium in which light travels with a speed of 1.4 x 108 m\s.
Ans. Laws of refraction of light:
First law: The incident ray, the refracted ray, and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
Second law (Snell’s law): The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is a constant for a given pair of media.
i.e., 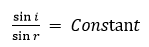
Speed of light in vacuum, c = 3 x 108 m\s
speed of light in medium, v = 1.4 x 108 m\s
Absolute refractive index = 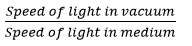
= 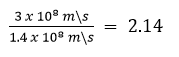
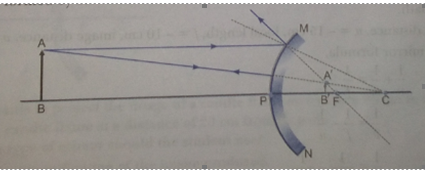
Que 8. The two positions in which a concave mirror produces a magnified image of given object. List two differences between the two images.
Ans. A concave mirror produces a magnified image when the object is placed in front of the mirror:
(i) between its pole and focus
(ii) between the focus and centre of curvature
In case (i) the image is virtual and erect, whereas in case (ii) the image is real and inverted.
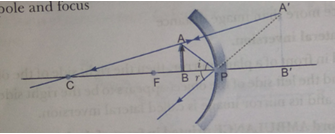
Que 9. The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is +3. Analyse this value and state the (i) type of mirror and (ii) position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
Ans. (i) Concave mirror
(ii) Between the pole and focus
Que 10. What will happen to a ray of light when it falls normally on a surface? Show it diagrammatically.
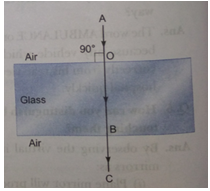
Ans. When a ray of light falls normally on the surface of a medium, then, no bending of light ray occurs. It means the light ray goes straight from one medium to another.
Que 11. Identify the device used (a spherical mirror or lens) in following cases, when the image formed is virtual and erect in each case.
(a) Object is placed between device and its focus, image formed is enlarge and its focus, image formed is enlarged and behind it.
(b) Object is placed between the focus and device, image formed is enlarged and on the same side as that of the object.
(c) Object is placed between infinity and device, image formed is diminished and between focus and optical centre on the same side as that of the object.
(d) Object is placed between infinity and device, image formed is diminished and between pole and focus, behind it.
Ans. (a) Concave mirror (b) Convex lens
(c) Concave lens (d) convex mirror
Que 12. A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?
Ans. Statement is correct if the object is placed within 20 cm from the lens in the first case and between 20 cm and 40 cm in the second case.
Que 13. How are power and focal length of a lens related? You are provided with two lenses of focal length 20 cm and 40 cm respectively. Which lens will you use to obtain more convergent light?
Ans. 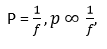
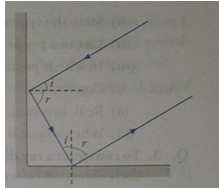
Que 14. Under what condition in an arrangement of two plane mirrors, incident ray and reflected ray will always be parallel to each other, whatever may be angle of incidence. Show the same with the help of a ray diagram.
Ans. When two plane mirrors are placed at right angle to each other, then the incident and reflected rays will always be parallel to each other.
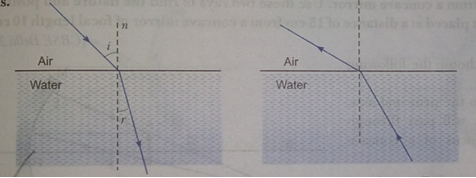
Que 15. Draw a ray diagram showing the path of rays of light when it enters with oblique incidence (i) from air into water; (ii) from water into air.
Ans.
Que 16. List two properties of the image formed by convex mirrors, Draw ray diagram in support of your answer.
Ans. The images formed by mirrors are: Virtual, erect and smaller than the object