Short Answer Questions - I - 2 Marks
Que 1. Explain why the surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time.
Ans. The surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time due to the formation of a thin layer of oxide, carbonate or sulphide on their surface by the slow action of the various gases present in air.
Que 2 Give two each of the metals that are good conductors and poor conductors of heat
respectively.
Ans. (a) Good conductors: Ag and Cu
(b) Poor conductors: Pb and Hg
Que 3. Name one metal and one non-metal that exist in liquid state at room temperature. Also name two metals having melting point less than 310 K (370 C).
Ans. Metal: Mercury (Hg); Non-metal: Bromine (Br)
Two metals with melting points less than 310K are Cesium (Cs) and Gallium (Ga).
Que 4. A zinc plate was kept in a glass container having copper sulphate solution. On examining it was found that the blue colour of the solution is getting fader and fader. After a few days when the zinc plate was taken out of the solution, a number of small holes were noticed in it. State the reason and give chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Ans. Zinc is more reactive than copper. Hence, when a zinc plate is kept in a solution of copper sulphate, it slowly displaces copper from the solution and blue colour of the solution keeps fading away. Because of zinc going into solution as zinc sulphate a number of holes are seen in the zinc plate. The reaction is
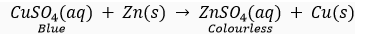
Que 5. Generally, when metals are treated with mineral acids, hydrogen gas is liberated but when metals (except Mn and Mg) are treated with HNO3, hydrogen is not liberated, why?
Ans. It is because HNO3 is a strong oxidisings agent. It oxidises the H2 produced to H2O and itself get reduced to any of the oxides of the nitrogen, like NO2, NO, etc.
Que 6. Metals replace hydrogen from dilute acids, whereas non-metals do not. Why?
Ans. Hydrogen from dilute acids can only be replaced if electrons are supplied to H+ ions of the acid,
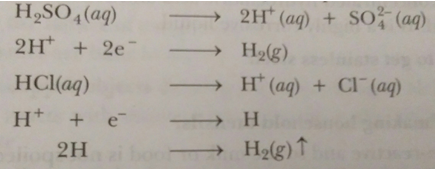
Que 7. What happens when
(i) Iron nail is placed in silver nitrate solution?
(ii) Iron strip is dipped in zinc sulphate solution?
Ans. (i) Iron is more reactive than silver.
Fe(s) + 2AgNO3 (aq)  Fe(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Fe(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
(ii) Iron is below zinc in the reactivity series; therefore, iron cannot displace zinc from zinc sulphate solution. No reaction takes place.
Que 8. Why do metals not evolve hydrogen gas with nitric acid?
Ans. When metal reacts with nitric acid (HNO3), hydrogen gas is not evolved. This is because HNO3 is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises H2 produced to water and is itself reduced to any of the oxides of nitrogen (N2O, NO or NO2). For example,
3Cu(s) + 8HNO3 (aq)  3Cu (NO3)2(aq) + 2NO (g) + 4H2O (l)
3Cu (NO3)2(aq) + 2NO (g) + 4H2O (l)
Que 9. (i) Name a metal for each case:
(a) It does not react with cold as well as hot water but reacts with steam.
(b) It does not react with any physical state of water.
(ii) When calcium metal is added to water the gas evolved does not catch fire but the same gas evolved on adding sodium metal to water catches fire. Why is it so?
Ans. (i) (a) Aluminium, (b) Copper
(ii) In both cases, the gas evolved is H2. When calcium reacts with water the heat evolved is not sufficient for hydrogen to catch fire. On the other hand, sodium metal reacts with water violently and in this case a lot of heat is evolved which is sufficient for hydrogen to catch fire.
Que 10. Which of the following reactions will not occur? Give reasons.
(i) MgSO4 (aq) + Fe(s) FeSO4 (aq) + Mg(s)
FeSO4 (aq) + Mg(s)
(ii) MgSO4 (aq) + Cu(s) CuSO4 (aq) + Mg(s)
CuSO4 (aq) + Mg(s)
(iii) CuSO4 (aq) + Fe(s)  FeSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
FeSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
Ans. Reaction (i) will not occur because Fe is less reactive than Mg. Reaction (ii) will not occur because Cuis less reactive than Mg.
Que 11. List any two observations when a highly reactive metal is dropped in water.
Ans. (i) Large amount of heat is evolved.
(ii) Metal starts floating.
Que 12. State the reason for the following behaviour of zinc metal:
On placing a piece of zinc metal in a solution of mercuric chloride, it acquires a shining silvery surface but when it is placed in a solution of magnesium sulphate no change is observed.
Ans. When a piece of zinc metal is placed in a solution of mercuric chloride (HgCl2).a white layer of mercury is deposited on zinc metal to give it silvery shining look. This is because mercury is lower to zinc in reactivity series and hence, zinc can displace mercury from HgCl2.
But when zinc is placed in a solution of magnesium sulphate, there is no change. This is because magnesium is above zinc in the reactivity series and hence, zinc cannot displace magnesium from its salt solution.
Que 13. An ore gives carbon dioxide on treatment with a dilute acid. What steps will you take to convert such a concentrated ore into free metal?
Ans. A metal carbonate reacts with a dilute acid to form carbon dioxide. Therefore, this ore is a carbonate ore. Carbonate ore is converted into free metal in the following two steps:
(i) Calcination: The carbonate ore is strongly heated in the absence of air to get the metal oxide.

(ii) Reduction: The metal oxide is reduced with carbon to get free metal.

Que 14. The following reaction takes place when aluminium powder is heated with MnO2.
3MnO2(s) + 4Al(s)  3Mn (l) + 2Al2O3 (l) + Heat
3Mn (l) + 2Al2O3 (l) + Heat
(a) Is aluminium getting reduced?
(b) Is MnO2 getting oxidised?
Ans. (a) No, because oxygen is added to aluminium therefore, it is getting oxidised.
(b) No, since manganese has lost oxygen therefore, it is getting reduced.
Que 15. What is a Thermit reaction? State one use of this reaction.
Ans. The reaction between iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3) and aluminium gives out lots of heat.
It is called the Thermit reaction.
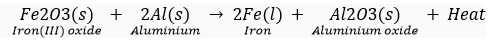
This displacement reaction is used to join railway tracks on cracked machine parts.
This heat gives out in the reaction melts the iron formed. The molten iron runs down between the tracks and welds them together.
Que 16. Why should the metal sulphides and carbonates be converted to metal oxides in the process of extraction of metal from them?
Ans. It is easier to obtain metal from its oxide, as compared from its sulphides and carbonates. So prior to reduction, sulphide ores are converted into oxides by roasting and carbonate ores by calcination.
Que 17. What is 24-carat gold? How will you convert it into 18-carat gold?
Ans. 24-carat gold is pure gold. Pure gold is very soft and not suitable for making jewellery. Therefore, to increase its hardness, it is alloyed either with copper or sılver.
18-carat gold is prepared by alloying 18 parts pure gold with 6 parts of either copper or silver.
Que 18. What would happen to iron railings on the road side if they are not painted? Why does it happen so?
Ans. If the iron railing on the road side is not painted, a brown rust would form on its surface because the moist air of the atmosphere reacts with iron to form brown flaky substance on its surface. The rust is hydrated iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3.xH2O.
Que 19. Explain why, the galvanised iron article is protected against rusting even if the zinc layer is broken.
Ans. The galvanised iron article is protected against rusting even if the zinc layer is broken because zinc is more easily oxidised than iron. So when zinc layer on the surface of galvanised iron article is broken, then zinc continues to corrode but iron article does not corrode or rust.
Que 20. Why is aluminium oxide considered an amphoteric oxide?
Ans. Aluminium oxide (Al2O3) shows basic as well as acidic behaviour because it reacts with both acids and bases. Thus, it is considered an amphoteric oxide. The two types of reactions given by Al2O3 are as follows:
(i) 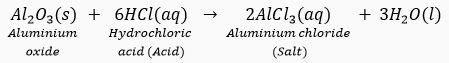
In this reaction, Al2O3 behaves as a basic oxide because it reacts with an acid to form salt and water.
(ii) 
Que 21. Why are food cans tin- Plated instead of zinc plated though zinc is cheaper than tin?
Ans. Tin is less reactive zinc. It is less likely to dissolve in the liquid strored in the food cans. Tin reacts only with powerful acids whereas zinc can easily react even with tomatoes, so it is ot safe to store food in zinc- plated cans.

