Long Answer Questions - 5 Marks
Que 1. The potential difference between two points in an electric circuit is 1 volt. What does it mean?
Name a device that helps to measure the potential difference across a conductor.
(ii) Why does the connecting cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
(iii) Electrical resistivities of some substances at 20° C are given below:
Silver 1.60× 10-8 Ω m
Copper 1.62 × 10-8 Ω m
Tungsten 5.2 x 10-8 Ω m
Iron 10.0 x 10-82 m
Mercury 94.0× 10-8 Ω m
Nichrome 100 × 10-6 Ω m
Answer the following questions using above data:
(a) Among silver and copper, which one is a better conductor? why?
(b) Which material would you advise to be used in electrical heating devices and why?
Ans. (i) The potential difference between two points is 1 volt means that if a charge of 1 coulomb is moved from one point to the other, 1 joule of work is required.
The potential difference across a conductor is measured by means of an instrument called the “voltmeter."
(ii) The electric power P is given by
P = I2 R
The resistance of the heating element is very high. Large amount of heat generates in the heating element and it glows hot.
The resistance of connecting cord is very low. Thus, negligible heat generates in the connecting cord and it does not glow.
(iii) (a) Silver is a better conductor due to its lower resistivity.
(b) Nichrome should be used in electrical heating devices due to very high resistivity.
Que 2. (a) Name an instrument that measures electric current in a circuit. Define the unit of electric current.
(b) What do the following symbols represent in a circuit diagram?

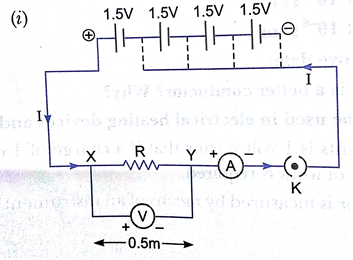
(c) An electric circuit consisting of a 0.5 m long nichrome wire XY, an ammeter, a voltmeter, four cells of 1.5 V each and a plug key was set up.
(i) Draw the electric circuit diagram to study the relation between the potential difference maintained between the points ‘X’, and ‘Y’, and the electric current flowing through XY.
(ii) Following graph was plotted between V and I values using above circuit:
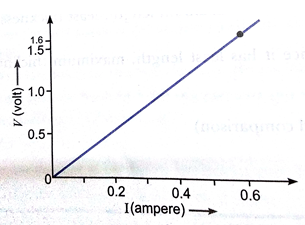
What would be the values of 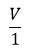
 ratios when the potential difference is 0.8 V, 1.2 V and 1.6 V respectively? What conclusion do you draw from these values?
ratios when the potential difference is 0.8 V, 1.2 V and 1.6 V respectively? What conclusion do you draw from these values?
Ans. (a) An instrument that measures electric current in a circuit is called "ammeter". The unit of electric current is ampere (A). 1 ampere is constituted by the flow of 1 coulomb of charge through any point in an electric circuit in 1 second.

Variable resistance or rheostat Plug key or switch (closed)
(c)
(ii) Following graph was plotted between V and I values.
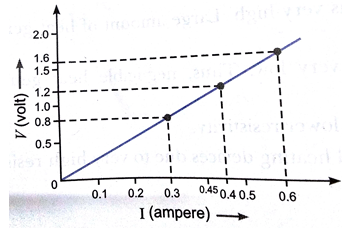
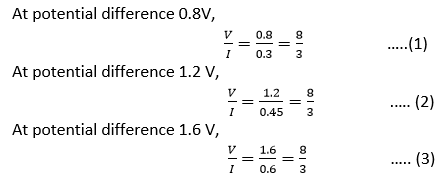
Conclusion: If I be the current through XY resistor and V be the potential difference across it, then the ratio 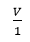 constant.
constant.
 V
V  I and Ohm’s
I and Ohm’s
Law is obeyed.
Que 3. Find out the following in the electric circuit given in figure alongside:
(a) Effective resistance of two 8 Ω resistors in the combination
(b) Current flowing through 4 Ω resistor
(c) Potential difference across 4 Ω resistance
(d) Power dissipated in 42 resistor
(e) Difference in ammeter readings, if any
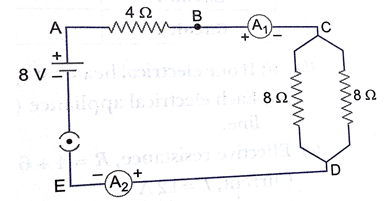
Ans. (a) 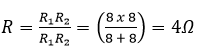
(b) 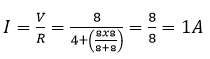
(c) V = I R = 1 x 4 = 4V
(d) P = I2 R = 12 x 4 = 4W
(e) No difference, same current flows through each element in a series circuit.
Que 4. Figure shows two electrical circuits.
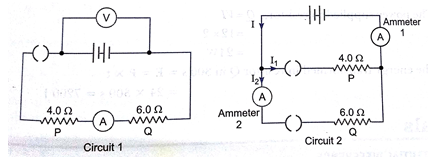
The batteries in circuit 1 and circuit 2 are identical.
(a) Put ticks in the table below to describe the connections of the two resistors P and Q.
|
|
Series |
Parallel |
|
Circuit 1 |
|
|
|
Circuit 2 |
|
|
(b) The resistor P and Q are used as small electrical heaters.
State two advantage of connecting them as shown in circuit 2.
(c) In circuit 1, the ammeter reads 1.2A when the switch is closed.
Calculate the reading of the voltmeter in this circuit.
(d) The two switches in circuit 2 are closed. Calculate the combined resistance of the two resistors in this circuit.
(e) When the switches are closed in circuit 2, ammeter 1 reads 5 A and ammeter 2 reads 2A. Calculate
(i) the current in resistor P,
(ii) the power supplied to resistor Q,
(iii) the energy transformed in resistor Q in 300s.
Ans. (a)
|
|
Series |
Parallel |
|
Circuit 1 |
Right |
|
|
Circuit 2 |
|
Right |
(b) (i) If one electrical heater stops working due to some defect then other keeps working normally.
(ii) Each electrical appliance (heater) gets the same voltage (220 v) as that of the power supply line.
(c) Effective resistance, R = 4 + 6 = 10 Ω
Current, I = 1.2 A
V = IR = 1.2 x 10 = 12 V
Voltmeter reading = 12 V
(d) Combined resistance,
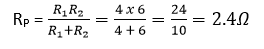
(e) Current I = 5 A
I2 = 2 A
(i) The current in resistor P = I1 = I – l2
= 5A – 2A
= 3A
(ii) The Power supplied to resistor, Q = VI
= 12 x 2
= 24 W
(iii) The energy transformed in resistor Q in 300 s = E = P x t
= 24 x 300s = 7200 J

