Long Answer Questions - 5 Marks
Que 1. Differentiate between tropic and nastic movements in plants.
Ans.
|
Tropic movements |
Nastic movements |
|
1. It can be easily observed in stems and roots.
4. Example: Bending of root towards gravity and shoot towards light. |
1. It is clearly observed in bilaterally symmetrical organs such as leaves and petals of flowers. 2. The movements occur due to stimulus of light and temperature.
4. Example: Leaves of ‘touch-me-not’ plant bend and droop on touching. |
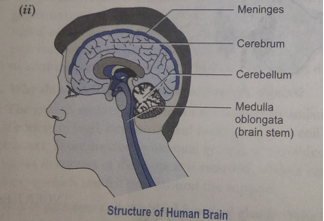
Que 2. (i) What are cranial and spinal nerves? Describe a spinal nerve.
(ii) Draw a diagram of the human brain and label the following parts:
(a) Cerebrum (b) Meninges
(c) Medulla oblongata (d) Cerebellum
Ans. (i) Cranial nerves arise in pairs from the various parts of brain and are 12 pairs in number.
Spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord in 31 pairs.
Spinal nerve arises in the form of dorsal root and ventral root and both unite in the neural canal to form a single branch. It comes out of the vertebral column through intervertebral canal and then divides into dorsal, ventral and visceral branches.
Que 3. Which hormone is released into the blood when its sugar level rises? Name the organ which produces the hormone and describe its effect on blood sugar level. Also name one digest enzyme that this organ secretes and the function of this enzyme.
Ans. Insulin hormone is released into the blood when its sugar level rises. Pancreas secrets the insulin hormone. The function of insulin hormone is to lower the blood sugar level. Deficiency of insulin hormone in the body causes a disease known as diabetes is characterised by large quantities of sugar in the blood. The insulin hormone controls the metabolism of sugar. If due to some reason, pancreas does not produce and secrete sufficient amount of insulin into blood, then the sugar level in the blood rises. The high sugar level in the blood can cause many harmful effects to the body of person. The person having severe diabetes are treated by giving injection of insulin. The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which contains enzymes like trypsin for digesting proteins, lipase for breakdown of emulsified fats and amylase for breakdown of starch.
Que 4. Describe the central nervous system in human beings.
Ans. The central nervous system in human beings consists of brain and spinal cord.
(i) Brain: Brain is the highest coordinating centre in the body. It is covered by meninges, which is made up of three layers. It is protected by cranium. Brain is broadly divided into:
(a) Forebrain: The forebrain includes cerebrum and olfactory lobes. Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Sensory and motor receptors are present in the brain. There are various regions for reception of vision (occipital lobe), reception of sound (temporal lobe), touch, smell, temperature (parietal lobe) and muscular activities (frontal lobe). Olfactory lobes are one in pair and receives olfactory nerves.
(b) Midbrain: It is the small portion of the brain that connects cerebrum with the other parts of the brain and spinal cord.
(c) Hindbrain: It consists of cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata. Cerebellum is responsible for coordination and adjustment of movement and posture. Pons regulate respiration. Medulla oblongata regulates swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomiting.
(ii) spinal cord: Medulla oblongata extends downwards, enclosed in vertebral column to form a cylindrical structure known as spinal cord. It is also covered by meninges. It is the reflex centre of the body.
Que 5. Give the various functions performed by the plant hormones.
Ans. The various functions performed by the plant hormones are:
(i) Auxins promote cell enlargement and cell differentiation. They also promote growth.
(ii) Gibberellins promote cell enlargement and cell differentiation in the presence of auxịn. It also help in breaking the dormancy in seeds and buds. It promote the growth in fruits.
(iii) Cytokinins promote cell division and help in breaking the dormancy of seeds and buds. It delay the ageing in leaves. It promotes the opening of stomata and also fruit growth.
(iv) Abscisic acid promotes the dormancy in seeds and buds. It promotes the closing of stomata and falling of leaves. Inhibits growth, reverses the growth promoting effects of auxins and gibberellins. Its effects include wilting of leaves.
(v) Ethylene promotes the falling of leaves, ripening of fruits and helps in breaking bud dormancy.
Que 6. What is reflex action? Explain with the help of examples.
Ans. A reflex action is defined as a spontaneous, automatic and mechanical response to a stimuli without the will of an individual. In such actions there is no involvement of the brain. All reflex actions are conveyed through the spinal cord by a path called reflex arc.
The reflex action travels in the following sequence:
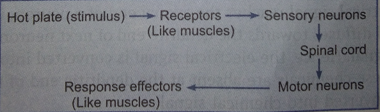
The reflex arc constitutes the following components:
(i) A receptor to perceive the stimulus.
(ii) A sensory or afferent nerve which carries the message from the receptor to the spinal cord.
(iii) The neurons of spinal cord transmit the impulse from afferent neurons to efferent neurons.
(iv) The motor or efferent nerve carries messages from spinal cord to the muscles (effectors) that show the response.
Some examples of reflex actions are:
(i) Blinking of eyes when a foreign particle gets in them.
(ii) Sneezing if an unwanted particle enters the nose.
(iii) Watering of mouth at the sight or smell of good food.
(iv) Withdrawal of foot while walking if a nail comes in the way and pricks the foot.
(v) Immediate withdrawal of hand of a person if some hot thing touches it.
Que 7. With the help of an activity demonstrate geotropism in plants.
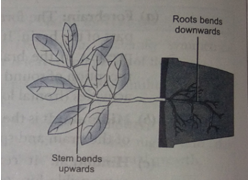
Ans. 1. Soak some seeds of gram or moong in water for one day.
2. Pierce slightly big holes (2 mm diameter) at the bottom of the cup.
3. Fill it with 1 cm thick layer of garden soil.
4. Sprinkle soaked seeds (moong/gram) over the soil. Water the seeds.
5. Put the cup on 2 pieces of wooden or stone slabs so that there is a little gap between the top of the table and bottom of the cup.
6. Cover the lower part of the set-up with black paper.
7. Water the seeds regularly with little water.
8. You will observe that the roots come out from the holes and grow towards the Earth showing positive geotropism.

