Long Answer Questions - 5 Marks
Que 1. (a) How do you calculate the valency of an element from its electronic configuration?
(b) What is the valency of magnesium with atomic number 12 and sulphur with atomic number 16?
(e) How does the valency vary in a period on going from left to right?
(d) How does the valency vary in going down a group?
Ans. (a) The valency of an element is determined by the number of valence electrons present in the outermost shell of its atom. The number of electrons lost or gained (or shared) by one atom of an element to achieve the nearest inert gas electron configuration, gives us the valency of the element.
(b) (i) Atomic number of magnesium = 12
Electronic configuration is 2, 8, 2.
A magnesium atom can lose its 2 valence electrons to achieve the inert gas electronic configuration of neon (2, 8).
Therefore, valency of magnesium = 2.
(ii) The atomic number of sulphur = 16.
Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 6.
A sulphur atom cannot lose 6 electrons to achieve inert gas electronic configuration due to energy consideration. It can gain 2 electrons to achieve the nearest inert gas electronic configuration of argon (2, 8, 8).
Thus, the valency of sulphur 2.
(c) On going from left to right along a period (short period), the valency of elements increases from 1 to 4 and then decreases to 0 (zero).
|
Third Period |
Na |
Mg |
Al |
Si |
P |
S |
Cl |
Ar |
|
Valency |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
(d) All the elements in a group have the same valency.
Que 2. An element placed in 2nd Group and 3rd Period of the Periodic Table, burns in presence of oxygen to form a basic oxide.
(a) Identify the element.
(b) Write the electronic configuration.
(c) Write a balanced equation when it burns in the presence of air.
(d) Write a balanced equation when this oxide is dissolved in water.
(e) Draw the electron dot structure for the formation of this oxide.
Ans. (a) Magnesium (Mg)
(b) K, L, M
2, 8,2
(c) 2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
(d) MgO(s) + H2O(l) → Mg (OH)2 (aq)
(e) 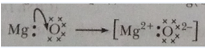
Que 3. Atomic number of a few elements are given below:
10, 20, 7, 14
(a) Identify the elements.
(b) Identify the Group number of these elements in the Periodic Table.
(c) Identify the Periods of these elements in the Periodic Table.
(d) What would be the electronic configuration for each of these elements?
(e) Determine the valency of these elements.
Ans. (a) Elements — Neon (Ne), Calcium (Ca), Nitrogen (N). Silicon (Si)
(b) Group — 18, 2, 15, 14
(c) Period — 2, 4, 2, 3
(d) Electronic configuration — (2, 8); (2, 8, 8, 2); (2, 5); (2, 8, 4)
(e) Valency — 0, 2, 3, 4
Que 4. Mendeléev predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium.
(a) Name the elements which have taken the place of these elements.
(b) Mention the Group and the Period of these elements in the Modern Periodic Table.
(c) Classify these elements as metals, non-metals or metalloids.
(d) How many valence electrons are present in each one of them?
Ans. (a) Germanium (Ge) and Gallium (Ga)
(b) Group 14; Period 4 and Group 13; Period 4
(c) Ge — Metalloid; Ga — Metal
(d) Ga — 3; Ge — 4
Que 5. An element X which is a yellow solid at room temperature shows catenation and allotropy. X forms two oxides which are also formed during the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals and are the major air pollutants.
(a) Identify the element X.
(b) Write the electronic configuration of X.
(c) Write the balanced chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals.
(d) What would be the nature (acidic/basic) of oxides formed?
(e) Locate the position of the element in the Modern Periodic Table.
Ans. (a) Element X is sulphur (atomic no. 16)
(b) K, L, M
2, 8, 6
(C) 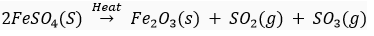
(d) Acidic
(e) 3rd period, group 16
Que 6. An element X of group 15 exists as diatomic molecule and combines with hydrogen at 773 K in presence of the catalyst to form a compound, ammonia which has a characteristic pungent smell.
(a) Identify the element X. How many valence electrons does it have?
(b) Draw the electron dot structure of the iatomic molecule of X. What type of bond is formed in it?
(c) Draw the electron dot structure for ammonia. What type of bond is formed in it?
Ans. (a) Nitrogen (atomic no. 7)
Electronic configuration: 2, 5; it has 5 valence electrons.
(b) 
(c) 
Que 7. Give an account of the process adopted by Mendeléev for the classification of elements. How did he arrive at "Periodic Law"?
Ans. (i) When Mendeléev started his work, 63 elements were known. He studied the compounds of these elements with oxygen and hydrogen. He selected hydrogen and oxygen as they are very reactive and formed compounds with most elements. The formulae of the hydrides and oxides formed by an element were treated as one of the basic properties of an element for its classification.
(ii) Elements with similar properties were arranged in a group.
(iii) Mendeléev observed that elements were automatically arranged in the order of increasing atomic masses.
Que 8. The atomic number of an element "X' is 19.
(a) Write its electronic configuration.
(b) To which period of the Modern Periodic Table does it belong and what is its valency?
(c) If ‘X’ burns in oxygen to form its oxide, what will be its nature-acidic, basic or neutral?
(d) Write balanced chemical equation for the reaction when this oxide is dissolved in water.
Ans. (a) Configuration of X (19) = 2,8,8,1.
(b) It belongs to fourth period and its valency is 1.
(c) Basic oxide (X2O)
(d) X2O+H2O → 2XOH
Que 9. (a) How does the atomic radius change as you go
(i) from left to right in a period?
(ii) down a group in the periodic table?
(b) Two elements X and Y have atomic numbers 12 and 16 respectively. Write the electronic configuration for these elements. To which period of the Modern Periodic Table do these two elements belong? What type of bond will be formed between them and why?
Ans. (a) (i) Atomic radius decreases.
(ii) Atomic radius increases.
(b) Atomic number of element X = 12
Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 2
K L M
Atomic number of element Y = 16
Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 6
K L M
The period number of an element is equal to the number of electron shells in its atom. These two elements have 3 electron shells, therefore they belong to 3rd period.

They will form ionic bond because X is a metal and Y is a non-metal. X loses two electrons which will be gained by Y.
Que 10. (a) How would the tendency to lose electrons change as you go
(i) from left to right across a period?
(ii) down a group?
(b) An element X (2, 8, 2) combines separately with (NO3)-,(SO4)2- and (PO4)3- radicals. Write the formulae of the three compounds so formed. To which group of the periodic table does the element "X' belong? Will it form covalent or ionic compound? Why?
Ans. (a) (i) Tendency to lose electrons decreases.
(ii) Increases.
(b) The three compounds are X(NO3)2, XSO4 and X3(PO4)2.
Valence electrons of element X is 2. Therefore, element X belongs to group 2. It will form ionic compounds because X loses 2 electrons to achieve the electronic configuration of inert gas and forms a positively charged ion.
Que 11. The position of eight elements in the Modern Periodic Table is given below where atomic numbers of elements are given in the parenthesis.
|
Period No. |
||
|
2. |
Li (3) |
Be (4) |
|
3. |
Na (11) |
Mg (12) |
|
4. |
K (19) |
Ca (20) |
|
5. |
Rb (37) |
Sr (38) |
(i) Write the electronic configuration of Ca.
(ii) Predict the number of valence electrons in Rb.
(iii) What is the number of shells in Sr?
(iv) Predict whether K is a metal or a non-metal.
(v) Which one of these elements has the largest atom in size?
(vi) Arrange Be, Ca, Mg and Rb in the increasing order of the size of their respective atoms.
Ans. (i) Electronic configuration of Ca -2, 8, 8, 2
(ii) Valence electrons in Rb is 1.
(iii) Five
(iv) Metal
(v) Rb is biggest in size.
(vi) Be < Mg < Ca < Rb
Que 12. Atoms of eight elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H have the same number of electronic shells but different number of electrons in their outermost shell. It was found that elements A and G combine to form an ionic compound which can also be extracted from sea water. This compound is added in a small amount to almost all vegetable dishes during cooking. Oxides of elements A and B are basic in nature while those of E and Fare acidic. The oxide of D is almost neutral. Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
(i) To which group or period of the periodic table do the listed elements belong?
(ii) What would be the nature of compounds formed by a combination of elements B and F?
(iii) Which two of these elements could definitely be metals and which are likely to be non-metals?
(iv) Which one of the eight elements is most likely to be found in gaseous state at room temperature?
(v) If the number of electrons in the outermost shell of elements C and G be 3 and 7 respectively, write the formula of the compound formed by the combination of C and G.
(v) Which one of the eight elements is likely to be a noble gas?
(vii) Which one of the eight elements would have the largest atomic radius?
(viii) Which one of these eight elements is likely to be a semi-metal or metalloid?
Ans. (i) Third period
Group-1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 respectively.
(ii) Nature of compound: Electrovalent/ionic
(iii) Metals-A and B; Non-metals - E, F, G
(iv) G/H (v) CG3
(vi) H (vii) A
(viii) D
Que 13. Atoms of seven elements A, B, C, D, E, F and G have a different number of electronic shells but have the same number of electrons in their outermost shells. The elements A and C combine with chlorine to form an acid and common salt respectively. The oxide of element A is liquid at room temperature and is a neutral substance, while the oxides of the remaining six elements are basic in nature. Based on the above information answer the following questions:
(i) What could the element A be?
(ii) Will elements A to G belong to the same period or same group of the periodic table?
(iii) Write the formula of the compound formed by the reaction of the element A with oxygen.
(iv) Show the formation of the compound by a combination of element C with chlorine with the help of electronic structure.
(v) What would be the ratio of number of combining atoms in a compound formed by the combination of element A with carbon?
(vi) Which one of the given elements is likely to have the smallest atomic radius?
Ans. (i) Hydrogen (ii) Same group
(iii) A2O/H20 (iv) 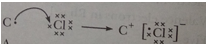
(v) 4 : 1 (vi) A
Que 14. In the following table, six elements A, B, C, D, E and F of the modern periodic table with atomic numbers 3 to 18 are given:
|
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
A |
G |
||||||
|
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
|
B |
C |
D |
F |
(a) Which of these is (i) Noble gas (ii) halogen?
(b) Which of these is the most active metal in 3rd period?
(c) Identify the most electronegative element in the third period
(d) In the compound between B and F what type of bond will be formed?
(e) What would be the nature of oxide formed by C?
Ans. (a) Noble gas - G
Halogen – F
(b) Most active metal – B
(c) Most electronegative in 3rd period – F
(d) Ionic bond
(e) Oxide formed by C would be bacis.

