Long Answer Questions - 5 Marks
Que 1. Both soap and detergent are some type of salts. What is the difference between them? Describe in brief the cleansing action of soap. Why do soaps not form lather in hard water? List two problems that arise due to the use of detergents instead of soaps.
Ans. Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. Detergents are generally ammonium or sulphonate salts of long chain carboxylic acids.
For cleansing action of soaps, refer to Q. 15 (NCERT Exercises)
Soaps do not form lather in hard water because hard water contains calcium and magnesium salts. Soap molecules react with calcium and magnesium salts to form an insoluble precipitate called scum.
Two problems which arise because of the use of detergents are:
(i) Detergents are non-biodegradable; hence, detergents accumulate in the environment and cause problems.
(ii) Certain phosphate additives are added to detergents which form a thick green scum over the river water and harm the animal life in the river.
Que 2. What happens when
(i) ethanol burns in air.
(i) ethanol reacts with sodium metal.
(iii) ethanol is oxidised with chromic anhydride in glacial ethanoic acid.
(iv) ethanol is heated with alkaline potassium permanganate.
(v) ethanol is heated with ethanoic acid in the presence of a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid?
Ans. (i) Ethanol is highly inflammable liquid. It catches fire easily and starts burning. Ethanol burns readily in air with a blue flame to form carbon dioxide and water vapour:
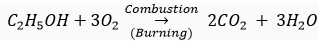
(ii) Ethanol reacts with sodium to produce sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas:
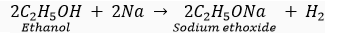
(iii) When ethanol is treated with chromic anhydride, then its partial oxidation takes place and ethanal is formed
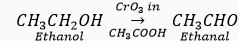
Chromic anhydride oxidises ethanol to ethanal.
(iv) Alkaline KMnO4 oxidises ethanol to ethanoic acid.
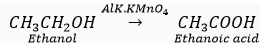
(v) Ethanol reacts with ethanoic acid in presence of concentrated sulphuric acid to form a sweet smelling ester, ethyl ethanoate.
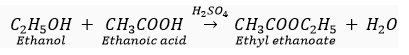
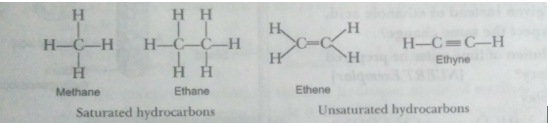
Que 3. (a) What are hydrocarbons? Give examples.
(b) Give the structural differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each. (c) What is a functional group? Give examples of four different functional groups.
Ans. (a) Compounds of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. For example, methane, ethane, etc.
(b) Saturated hydrocarbons contain carbon-carbon single bonds.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain at least one carbon-carbon double or triple bond.
(c) An atom/group of atoms joined in a specific manner which is responsible for the characteristic chemical properties of the organic compounds is called a functional group. Examples are hydroxyl group (-OH), aldehyde group (-CHO), ketonic group 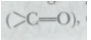 carboxylic group (
carboxylic group (
Que 4. Explain why carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bond. Explain in brief two main reasons for carbon forming a large number of compounds. Why does carbon form strong bonds with most other elements?
Ans. Carbon has 4 electrons in its outermost shell, and needs to gain or lose 4 electrons to attain noble gas configuration. Losing or gaining 4 electrons is not possible due to energy considerations, hence it shares electrons to form covalent bonds.
Two reasons for large number of carbon compounds:
(i) Catenation: The unique ability of carbon to form bonds with other atoms of carbon giving rise to long chains of different types of compounds.
(ii) Tetravalency: Since carbon has a valency of 4, it is capable of bonding with four other atoms of Carbon or atoms of elements like oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, etc.
carbon forms strong bonds with most other elements because of its small size which enables the nucleus to hold on to the shared pairs of electrons strongly.
Que 5. A compound C (molecular formula, C2H4O2) reacts with Na-metal to form a compound R and evolves a gas which burns with a pop sound. Compound C on treatment with an alcohol A in presence of an acid forms a sweet smelling compound S (molecular formula C3H6O2). On addition of NaOH to C, it also gives R and water. S on treatment with NaOH solution gives back R and A.
Identify C, R, A, S and write down the reactions involved.
Ans. C- Ethanoic acid
R- Sodium salt of ethanoic acid (sodium acetate) and gas evolved is hydrogen
A- Methanol
S- Ester (Methyl acetate)
(a) 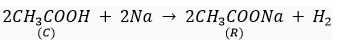
(b) 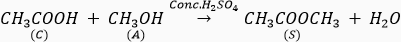
(c) 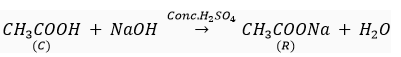
(d) 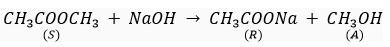
Que 6. Look at the figure and answer the following questions:
(a) What change would you observe in the calcium hydroxide solution taken in tube B?
(b) Write the reaction involved in A and B respectively.
(c) If ethanol is given instead of ethanoic acid, would you expect the same change?
(d) How can a solution of lime water be prepared in the laboratory?
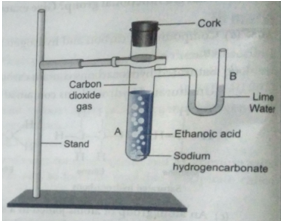
Ans. (a) It will turn milky.
(b) 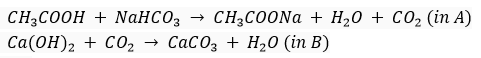
With excess CO2, milkiness disappears.
(c) As C2H5OH and NaHCO3 do not react, a similar change is not expected
C2H5OH + NaHCO3  No change
No change
(d) The lime water is prepared by dissolving calcium oxide in water and decanting the supernatant liquid.
Que 7. A salt X is formed and a gas is evolved when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen- carbonate. Name the salt X and the gas evolved. Describe an activity and draw the diagram of the apparatus to prove that the evolved gas is the one which you have named. Also, write chemical equation of the reaction involved
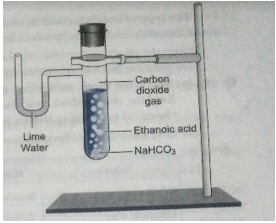
Ans. X is sodium ethanoate
Gas evolved is carbon dioxide
Activity:
(i) Set up the apparatus as shown in the figure.
(ii) Take a spatula-full of sodium hydrogencarbonate in a test tube and add 2 mL of dilute ethanoic acid.
(iii) We observe that brisk effervescence of a gas is produced in the test tube.
(iv) Now pass the gas produced through freshly prepared lime water.
It is observed that lime water turns milky. Only carbon dioxide gas can turn lime water milky. So this activity proves that when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogencarbonate, then carbon dioxide is evolved.
CH3COOH + NaHCO3  CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
Que 8. (i) Give a chemical test to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
(ii) Name the products formed when ethane burns in air. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction showing the types of energies liberated.
(iii) Why is reaction between methane and chlorine in the presence of sunlight considered a substitution reaction?
Ans. (i) Br2-water test: Br2-water is a brown coloured liquid.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons give addition reaction with Br2, so the colour of Br2- water gets decolourised.
Saturated hydrocarbons do not react with Br2-water, so the colour of Br2-water does not get decolourised
(ii) On burning ethane in air, the products obtained are carbon dioxide and water, along with heat and light.
2C2H6 (g) + 7O2 (g)  4CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l) + Heat + Light
4CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l) + Heat + Light
(iii) Methane reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight to form chloromethane and hydrogen chloride.

With the excess of chlorine, all the four hydrogen atoms of methane are replaced by chlorine atoms to form carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). This reaction is considered as substitution reaction because hydrogen of methane is substituted by chlorine.
Que 9. Elements forming ionic compounds attain noble gas electronic configuration by either gaining or losing electrons from their valence shells. Explain giving reason why carbon cannot attain such a configuration in this manner to form its compounds. Name the type of bonds formed in ionic compounds and in the compounds formed by carbon. Also explain with reason why carbon compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity.
Ans. Carbon has 4 electrons in its outermost shell. It cannot lose 4 electrons to form C4+ cation because
very high energy is required to remove 4 electrons leaving behind a carbon cation with 6 protons in its nucleus holding onto just 2 electrons. It also cannot gain 4 electrons to form C4 -anion because it is difficult for 6 protons to hold onto 10 electrons.
The type of bonds formed in ionic compounds are ionic or electrovalent bonds and in compounds formed by carbon are covalent bonds.
Since the electrons are shared, there are no charged particles in carbon compounds and hence they are poor conductors of electricity.
Que 10. (a) You have three unlabelled test tubes containing ethanol, ethanoic acid and soap solution. Explain the method you would use to identify the compounds in different test tubes by chemical tests using litmus paper and sodium metal.
(b) Give the reason of formation of scum when soaps are used with hard water.
Ans. (a)
|
Solution |
Blue Litmus Paper |
Red Litmus Paper |
Sodium Metal |
|
Ethanol |
No change |
No change |
Hydrogen gas |
|
Ethanoic acid |
Turns red |
No changes |
Hydrogen gas |
|
Soap |
No changes |
Turns blue |
Hydrogen gas |
(b) Hard water contains calcium ions or magnesium ions or both. These ions on reacting with soap solution forms insoluble substance called scum.

