Long Answer Questions - 5 Marks
Q. 1. Differentiate between a true solution and a colloid.
Ans.
|
True solution |
Colloid |
|
1. A true solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. 2. The size of the particles is less than one nanometer. 3. It is always transparent. 4. The particles cannot be seen even with microscope. 5. It does not show Tyndall effect. |
1. A colloidal solution is a heterogeneous mixture of two substances. 2. The range of particle size is between one nanometer to 1000 nanometer. 3. It is translucent. 4. The particles of a colloidal solution can be seen with microscope. 5. It shows Tyndall effect. |
Q. 2. Distinguish between physical change and chemical change.
Ans.
|
Physical change |
Chemical change |
|
1. In a physical change, only physical properties such as colour, physical state, density, volume, etc. change; chemical properties remain unchanged. 2. No new substance is formed in a physical change. 3. Very little or no energy in the form of heat, light or sound is usually absorbed or given out in a physical change. 4. A physical change is a temporary change. 5. The original form of substance can be regained by simple physical methods. 6. A physical change is reversible. |
1. In a chemical change, the chemical composition and chemical properties undergo a change. 2. A new substance is formed in a chemical change. 3. A chemical change is always accompanied by absorption or evolution of energy. 4. A chemical change is a permanent change. 5. Original substance cannot be obtained by simple physical methods. 6. A chemical change is irreversible. |
Q. 3. Distinguish between metals and non-metals.
Ans.
|
Metals |
Non-metals |
|
1. They have lustre (sheen). 2. They are malleable and ductile. 3. They have high density and high melting and boiling points. 4. Except mercury and gallium, all other metals are solid at room temperature. 5. They are sonorous. 6. They are good conductors of heat and electricity. 7. They are generally hard (except sodium and potassium). 8. They have high tensile strength. |
1. They are non-lustrous (dull). 2. They are neither malleable nor ductile. 3. They have low density and low melting and boiling points. 4. Non-metals may exist in solid, liquid or gaseous states at room temperature. 5. They are not sonorous. 6. They are poor conductors of heat and electricity. 7. Non-metals are generally soft (except diamond). 8. They have low tensile strength. |
Q. 4. Distinguish between compounds and mixtures.
|
Compounds |
Mixtures |
|
1. Compounds are formed as a result of chemical reactions between two or more elements or Compounds. 2. The components of a compound are always present in a definite ratio by mass. 3. The properties of a compound are entirely different from its constituents. 4. Compound are always homogeneous in nature. 5. Compound formation is accompanied by absorption or evolution of light, heat or electrical energy. 6. Melting and boiling points of a compound are usually sharp and fixed. 7. The constituents of a compound cannot be separated by physical or mechanical means. They can, however, be separated by chemical methods. |
1. Mixtures are formed by simply mixing two or more constituents. There are no chemical 2 The components of a mixture may be present in any ratio. 3. The properties of a mixture are same as those of its constituents. 4. Mixtures are usually heterogeneous (except in solutions). 5. Heat, light or electrical energy may not be evolved or absorbed during the formation of a mixture. 6. Melting and boiling points of a mixture are usually not sharp and fixed. 7. The components of a mixture can be easily separated by physical methods. |
Q. 5. A group of students took an old shoe box and covered it with a black paper from all sides. They fixed a source of light (a torch) at one end of the box by making a hole in it and made another hole on the other side to view the light. They placed a milk sample contained in a beaker/tumbler in the box as shown in the figure. They were amazed to see that milk taken in the tumbler was illuminated. They tried the same activity by taking a salt solution but found that light simply passed through it.
(a) Explain why the milk sample was illuminated. Name the phenomenon involved.
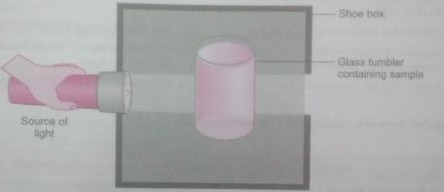
(b) Same results were not observed with a salt solution. Explain.
(c) Can you suggest two more solutions which would show the same effect as shown by the the milk solution?
Ans. (a) Milk is a colloid. If a beam of light is put on a milk sample contained in a beaker, the path of light beam is illuminated and becomes visible when see from the other side. This is because the colloidal particles are big enough to scatter light falling on them. This scattered light enters our eyes and we are able to see the path of light beam.
The scattering of light by colloidal particles is knows as Tyndall effect.
(b) Salt solation is a true solution. If a beam of light is put on a salt solution kept in a beaker in a dark room, the path of light beam is not visible inside the solution when see from the other side. This is because salt particles present in it are so small that they cannot scatter light rays falling on them.
(c) Detergent solution, sulphur solution.
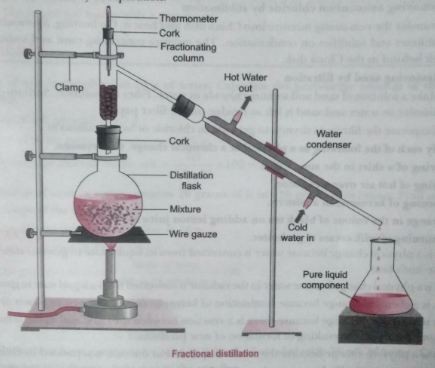
Q.6. Fractional distillation is suitable for separation of miscible liquids with a boiling point difference of about 25 K or less. What part of fractional distillation apparatus makes it efficient and possess an advantage over a simple distillation process? Explain using a diagram.
Ans. The fractionating column packed with glass beads provides a surface for the vapours to collide and lose energy so that they can be quickly condensed and distilled. Also, length of the column would increase the efficiency of separation.
Q.7. A child wanted to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. He marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in figure. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper.

(i) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components?
(ii) Name the technique used by the child.
(ii) Suggest one more application of this technique.
Ans.
(i) The colour component which is more soluble in water dissolves first, rises faster and produces a colour band (spot) on the paper at a higher position. The less soluble colour components dissolve a little later, rise slower and form coloured bands at lower heights. In this way, three different bands will be observed.
(ii) Chromatography
(iii) To separate the pigments presents in chlorophyll.
Q. 8. You are provided with a mixture containing sand, iron filings, ammonium chloride and sodium chloride. Describe the procedures you would use to separate these constituents from the mixture.
Ans. (i) Removing iron filings from the mixture by magnetic separation.
Take the mixture in a petri dish and roll a bar magnet over it. Iron filings will get attach to the magnet and thus separate from the mixture.
(ii) Removing ammonium chloride by sublimation.
Transfer the remaining mixture into China dish and heat it. On heating, ammonium chloride sublimes and solidifies on condensation. The mixture containing sand and sodium chloride left behind in the China dish.
(iii) Removing sand by filtration
Make a solution of sand and sodium chloride in water. Filter the solution. Sodium chloride will dissolve in water and sand is left as residue on the filter paper.
(iv) Evaporate the filtrate to dryness to get sodium chloride or by crystallisation.
Q. 9. Classify each of the following as a physical or a chemical change. Give reasons.
(a) Drying of a shirt in the sun.
(b) Rising of hot air over a radiator.
(c) Burning of kerosene in a lantern.
(d) Change in the colour of black tea on adding lemon juice to it.
(e) Churning of milk cream to get butter.
Ans.
(a) It is a physical change because water is converted from its liquid state to gaseous state because of the sun's heat.
(b) It is a physical change because water in the radiator is converted from a liquid state to gaseous state.
(c) It is a chemical change because combustion of kerosene occurs and new products are formed.
(d) It is a chemical change because there is a reaction between the citric acid in the lemon and the compounds of tea resulting in formation of new products.
(e) It is a physical change because the cream suspended in the milk is separated by churning.
Q. 10. Show diagrammatically how water is purified in the waterworks system and list the processes involved.
Ans.

Q. 11. Iron filings and sulphur were mixed together and divided into two parts ‘A and S, Part A, was heated strongly while Part 'S' was not heated. Dilute hydrochloric acid was added to both the parts and evolution of gas was seen in both the cases. How will you identify the gases evolved?
Ans.
Part A
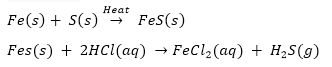
Part B
Fe(s) + S(s) → Mixture of iron filings and sulphur When dilute HCl is added to it Fe(s) + S(s) + 2HCI(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g) Sulphur remains unreacted. H2S gas formed has a foul smell and on passing through lead acetate solution, it turns the solution black. Hydrogen gas burns with a pop sound.

