Long Answer Questions - 5 Marks
Q. 1. Describe the continuous motion of particles of matter with the help of an activity.
Ans. (a) To demonstrate motion of particles in air:
- Place few lighted incense Sticks in a corner of a room.
- Move about the room and smell the fragrance of the incense sticks.
The fragrance produced due to burning of incense sticks is due to movement of vapours produced rapidly in all directions.
(b) To demonstrate motion of particles of solid matter:
(i) Drop a crystal of copper sulphate or potassium permanganate into a glass of hot water.
(ii) Do not stir the solution and allow the crystals to settle at the bottom.
(iii) The colour of the solid is seen spreading slowly. This is because the solid particles diffuse in the water.
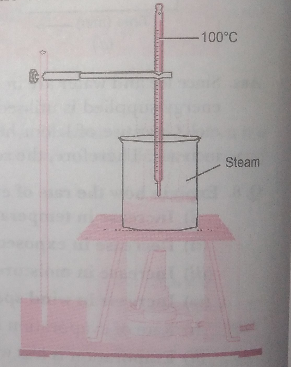
Q. 2. Describe an activity to determine the boiling point of water and melting point of ice.
Ans. Determination of boiling point of water:
- In a beaker take some water and insert a thermometer in it with the help of a clamp
- Put the beaker on a tripod stand and heat the apparatus with the help of kerosene burner slowly
- Observe what happens to water.
- You will observe a steady stream of bubbles. This temperature is the boiling point of water.
Determination of melting point of ice:
- Take crushed ice in a beaker and insert a thermometer in the beaker by hanging it from the clamp of the stand in such ay that the bulb of the thermometer is completely inside the ice.
- Wait for some time and keep recording the temperature after small intervals of time.
- Note down the temperature when ice just starts melting.
- Let the bulb of the thermometer remain in mixture of ice and water for some more time and keep recording the temperature. This temperature is the melting point of ice.
Q. 3. While heating ice in a beaker with a thermometer suspended in it, a student recorded the
following observations:
|
Time (in min.) |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
|
Temp. (in 0C) |
-3 |
-1 |
0 |
0 |
5 |
8 |
12 |
15 |
19 |
22 |
30 |
50 |
73 |
100 |
100 |
Based on the above observations, answer the following questions:
(a) State the change(s) observed between 2-3 min. and name the process involved.
(b) Between 30-35 min., the temperature remains constant. State the reason for this. Name the
heat involved in the process and define it.
Ans. (a) Between 2-3 min, ice converts into water. This process is known as fusion.
(b) Between 30-35 min, the temperature remains constant because the heat supplied is used up in overcoming the intermolecular forces of liquid to change into vapours. The heat involved in the process is latent heat of vaporisation. It is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of liquid into gas at its boiling point.
Q. 4. Discuss the various factors which affect the rate of evaporation. Latent heat of evaporation of two liquids A and B is 100 J/kg and 150 J/kg respectively. Which one can produce more cooling effect and why?
Ans. Factors affecting the rate of evaporation:
(a) Surface area: The rate of evaporation increases with increase in surface area.
(b) Temperature: The rate of evaporation increases with increase in temperature.
(c) Humidity: The rate of evaporation decreases with increase in humidity.
(d) Wind speed: The rate of evaporation increases with increase in wind speed.
(e) Nature of the liquid: The volatile compounds evaporate faster than less volatile compounds (liquids).
B will produce more cooling effect because it will absorb more heat from the surroundings for evaporation
Q.5. Comment on the following statements:
(a) Evaporation causes cooling.
(b) Rate of evaporation of an aqueous solution decreases with increase in humidity.
(c) Sponge though compressible is a solid.
(d) Ice is solid at 0°C, while water is liquid at room temperature.
(e) Sugar crystals dissolve faster in hot water than cold water.
Ans. (a) Evaporation produces cooling as the particles at the surface of the liquid gain energy from the surroundings and change into vapour, thereby producing a cooling effect.
(b) Air around us cannot hold more than a definite amount of water vapour at a given temperature which is known as humidity. So, if the air is already rich in water vapour, it will not take up more water; therefore, rate of evaporation of water will decrease.
(c) A sponge has minute holes in which air is trapped. Also the material is not rigid. When we press it, the air is expelled out and we are able to compress it. But it is a solid because it has definite shape and volume and does not change its shape unless compressed.
(d) Ice is solid at 00C because it has a definite volume and definite shape due to strong intermolecular forces. Water is liquid at room temperature because it has definite volume and no definite shape due to weak intermolecular forces of attraction.
(e) Sugar crystals dissolve faster in hot water than cold water because hot water molecules have more kinetic energy. Due to this, they strike faster on the particles of sugar than cold water molecules. As a result, hot water will dissolve them faster than cold water

